Mutual TLS for OAuth Clients¶
Mutual TLS is a widely-used, secure authentication technique that ensures the authenticity between a client and server using an encrypted channel established with a mutual X.509 certificate. The client certificate and certificate verification messages will be sent during the TLS handshake.
The TLS handshake is a set of steps executed to establish a secure connection between the client and server.
Mutual TLS is also used in the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework as a secure authentication mechanism.
Mutual TLS for OAuth client authentication can be implemented using either of the following mechanisms:
- PKI mutual TLS OAuth client authentication: This approach uses a subject Distinguished Name (DN) and validated certificate chain to identify the client.
- A self-signed certificate: In this approach, the client needs to register an X.509 certificate during the service provider configuration and import it to the truststore.
WSO2 Identity Server currently supports the approach that uses the self-signed certificates.
Let's try out configuring mutual TLS in WSO2 Identity Server and test with a sample.
Before you begin
-
Disable the mutual SSL authenticator: !!! warning The mutual SSL authenticator allows the OAuth client to access the WSO2 Identity Server admin services without having the required privileges. Open the
deployment.tomlfile in the<IS_HOME>/repository/conf/directory and add the following configuration.[admin_console.authenticator.mutual_ssl_authenticator] enable = false
- If WSO2 Identity Server is fronted by a load-balancer, enable SSL tunnelling.
Deploying and Configuring Mutual TLS Client Authenticator Artifacts¶
-
Open the
deployment.tomlfile in the<IS_HOME>/repository/conf/directory.-
Add
trustManagerClassName="org.wso2.carbon.identity.core.util.ClientAuthX509TrustManager" entry.[transport.https] trustManagerClassName="org.wso2.carbon.identity.core.util.ClientAuthX509TrustManager" -
MutualTLS supports two-way TLS authentication that allows the server to validate the client and vice versa. Certain applications, e.g., mobile applications may not require server-side validation.
To make the server-side validation optional, set the
clientAuthattribute towantin the same configuration similar to following.[transport.https] trustManagerClassName="org.wso2.carbon.identity.core.util.ClientAuthX509TrustManager" clientAuth="want"
-
-
Download Mutual TLS Client Authenticator v2.0.3 connector from here .
Note that an OSGI bundle (org.wso2.carbon.identity.oauth2.token.handler.clientauth.mutualtls-<VERSION>.jar) gets downloaded. -
Copy the OSGI bundle to the
<IS_HOME>/repository/components/dropinsdirectory. -
Open the
deployment.tomlfile in the<IS_HOME>/repository/conf/directory and add the following configuration.[[event_listener]] id = "custom_event_listener" type = "org.wso2.carbon.identity.core.handler.AbstractIdentityMessageHandler" name= "org.wso2.carbon.identity.oauth2.token.handler.clientauth.mutualtls.MutualTLSClientAuthenticator" order = 158 enable = true -
In order for mutual TLS authentication to work, the public certificates of the client application and authorization server (WSO2 Identity Server) should be imported to each other's truststores.
For demonstration purposes, let's assume that both the authorization server's truststore (
WSO2_TRUSTSTORE) and client's truststore (CLIENT_TRUSTSTORE) are in WSO2 Identity Server.-
Navigate to the
<IS_HOME>/repository/resources/securitydirectory in a command prompt.cd <IS_HOME>/repository/resources/security -
To generate the client's private key and public certificate, execute the following commands and enter Distinguished Name (DN) when prompted.
Format
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -x509 -keyout <CLIENT_PRIVATE_KEY> -out <CLIENT_PUBLIC_CERTIFICATE> -days <VALIDITY_PERIOD> -nodesExample
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -x509 -keyout key.pem -out client-certificate.pem -days 3650 -nodesNote
The
CLIENT_PRIVATE_KEYandCLIENT_PUBLIC_CERTIFICATEwill be used to generate the access token at a later step. -
To import the client's public certificate to the authorization server's truststore, execute the following command.
Format
keytool -import -trustcacerts -alias <CLIENT_PUBLIC_CERTIFICATE_ALIAS> -file <CLIENT_PUBLIC_CERTIFICATE> -keystore <WSO2_TRUSTSTORE> -storepass <WSO2_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD>Example
keytool -import -trustcacerts -alias client -file client-certificate.pem -keystore client-truststore.jks -storepass wso2carbon -
To export the public certificate of WSO2 Identity Server, execute the following command.
Format:
Format
keytool -export -alias <WSO2_CERTIFICATE_ALIAS> -file <WSO2_CERTIFICATE> -keystore <WSO2_KEYSTORE> -storepass <WSO2_KEYSTORE_PASSOWRD>Example:
Example
keytool -export -alias wso2carbon -file wso2-certificate.crt -keystore wso2carbon.jks -storepass wso2carbon -
Import the public certificate of WSO2 Identity Server to the client's truststore. If the truststore is using the jks format, execute the following command.
Format
keytool -import -trustcacerts -alias <WSO2_PUBLIC_CERTIFICATE_ALIAS> -file <WSO2_PUBLIC_CERTIFICATE> -keystore <CLIENT_TRUSTSTORE> -storepass <CLIENT_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD>Example
keytool -import -trustcacerts -alias wso2carbon -file wso2-certificate.crt -keystore truststore.jks -storepass client-password -
Click Update.
-
-
Restart WSO2 Identity Server.
Testing the Sample¶
Follow the steps below to test the configurations.
-
Create a service provider.
- Access the WSO2 Identity Server Management Console.
- On the Main menu, click Identity > Service Providers >
Add.

- Enter
playground2as the Service Provider Name and click Register.

-
Copy the content in your client application's certificate in PEM format into the Application Certificate text field.

!!! note Instead of uploading the service provider certificate as shown above, you can choose to use the JWKS enpoint as shown below and add the relevant JWKS URI.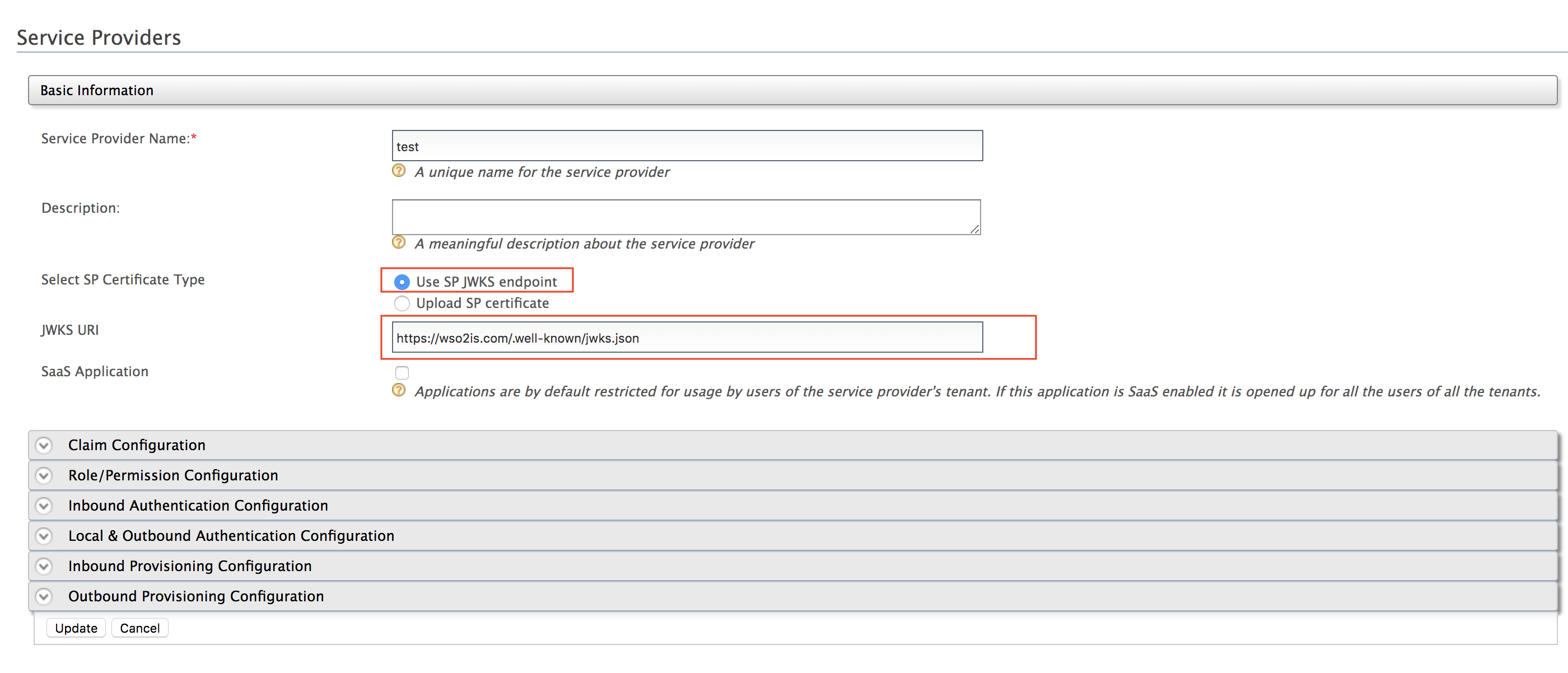 -
Expand Inbound Authentication Configuration > OAuth/OpenID Connect Configuration and click Configure.

- Enter
http://localhost:8080/playground2/oauth2clientas the Callback URL.

- Click Add.
Note that the OAuthclient keyandclient secretget generated.

-
To obtain an access token by invoking the OAuth token endpoint of WSO2 Identity Server, execute the following cRUL in a command prompt.
This request contains the client ID, client's public certificate and any other additional claims and is signed using the client's private key.
Format
curl -k -d "grant_type=password&username=<USERNAME>&password=<PASSWORD>&client_id=<CLIENT_KEY>" -H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" https://localhost:9443/oauth2/token -i --cert <CLIENT_PUBLIC_CERTIFICATE> --key <CLIENT_PRIVATE_KEY>Sample token request using mutual TLS client authentication
curl -k -d "grant_type=password&username=admin&password=admin&client_id=qiB6avlILBqnJLSxOfadoJYwOnQa" -H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" https://localhost:9443/oauth2/token -i --cert certificate.pem --key key.pemNote that an access token gets generated. You can use this access token to access the APIs or any other secured resources of the client application.
Sample response:
