Install WSO2 Identity Server¶
Prerequisites¶
Prior to installing any WSO2 Identity Server, it is necessary to have the appropriate prerequisite software installed on your system. Verify that the computer has the supported operating system and development platforms before starting the installation.
System requirements¶
Note
The below recommendations can change based on the expected concurrency & performance.
CPU |
4 vCPUs (x86_64 Architecture) |
|---|---|
Memory |
4 GB RAM |
Disk |
~ 10 GB disk space, excluding space allocated for log files and databases. |
Environment compatibility¶
Operating Systems/ Databases/ Userstores |
Note
|
|---|
Required applications¶
The following applications are required for running the product and its samples or for building from the source code.
Note
The applications marked with an asterisk * are mandatory.
Required applications to run the product
These applications are mandatory and are required to run the binary distribution of the WSO2 product. The binary distribution contains the binary files for both MS Windows, and Linux-based operating systems.
Application |
Purpose |
Version |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Java SE Development Kit (JDK)* |
|
|
|
Web Browser* |
Note: On Windows Server 2003, you must not go below the medium security level in Internet Explorer 6.x. |
|
Required applications to run samples and build from source
These applications are required for building the product from the source distribution, and compiling and running product samples.
Warning
If you are installing by downloading and extracting the binary distribution (as recommended for most users) instead of building from the source code, you do not need to install Maven.
| Application
|
Purpose | Version | Download Links |
|---|---|---|---|
Apache Maven |
|
3.0.x or later |
Install on different platforms¶
Install on Linux or OS X¶
Follow the instructions below to install WSO2 Identity Server on Linux or Mac OS X.
Install the required applications
-
Log in to the command line (Terminal on Mac).
-
Ensure that your system meets the Installation Prerequisites. Java Development Kit (JDK) is essential to run the product.
Install WSO2 Identity Server
- Download the latest version of WSO2 Identity Server.
-
Extract the archive file to a dedicated directory for WSO2 Identity Server, which will hereafter be referred to as
<IS_HOME>.Warning
If you are using Mac OS with High Sierra, you may encounter the following warning message when logging in to the management console due to a compression issue that exists in the High Sierra SDK.
WARN {org.owasp.csrfguard.log.JavaLogger} - potential cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attack thwarted (user:<anonymous>, ip:xxx.xxx.xx.xx, method:POST, uri:/carbon/admin/login_action.jsp, error:required token is missing from the request)To avoid this issue,
1. Open thedeployment.tomlfile in the<IS_HOME>/repository/conf/directory.
2. Set thecompressionelement under the HTTPS connector configuration tooffand restart WSO2 Identity Server.Note
If the above configuration is not listed in
deployment.toml, add the above configuration manually.
Set up JAVA_HOME
You must set your JAVA_HOME environment variable to
point to the directory where the Java Development Kit (JDK) is installed
on the computer.
Setting JAVA_HOME is a standard practice when you are using Java-based programs. You may not need to do this manually depending on your Java installer, as this variable is usually set by the Java installer itself. This guide is provided in case the JAVA_HOME variable has not been set or is incorrectly set on your machine.
Info
Environment variables are global system variables accessible by all the processes running in the operating system.
- In your home directory, open the BASHRC file (.bash_profile file on Mac) using a text editor such as vi, emacs, pico, or mcedit.
-
Assuming you have JDK 11.0.14 in your system, add the following two lines at the bottom of the file (Replace
/usr/java/jdk-11.0.14with the path of your JDK installation). directory where the JDK is installed.export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk-11.0.14 export PATH=${JAVA_HOME}/bin:${PATH}export JAVA_HOME=/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-11.0.14/Contents/Home -
Save the file.
Info
If you are not familiar with text editors in a Linux SSH session, run the
cat >> .bashrc.command on a terminal, paste the string from the clipboard and press Ctrl+D. -
To verify that the
JAVA_HOMEvariable is set correctly, execute the following command:echo $JAVA_HOMEwhich javaIf the above command gives you a path like /usr/bin/java, then it is a symbolic link to the real location. To get the real location, run the following:
ls -l `which java` -
The system returns the JDK installation path.
Set system properties
If you need to set additional system properties when the server starts, you can take the following approaches:
- Set the properties from a script : Setting your system properties in the startup script is ideal, because it ensures that you set the properties every time you start the server. To avoid having to modify the script each time you upgrade, create your own startup script that wraps the WSO2 startup script and add the properties you want to set, rather than editing the WSO2 startup script directly.
- Set the properties from an external registry : If you want to access properties from an external registry, you could create Java code that reads the properties at runtime from that registry. Be sure to store sensitive data such as username and password to connect to the registry in a properties file instead of in the Java code and secure the properties file with the cipher tool.
You are now ready to run the product.
Install on Solaris¶
Follow the instructions below to install Identity Server on Solaris.
Install the required applications
- Establish an SSH connection to the Solaris machine or log in on the text console.
- Be sure your system meets the Installation Prerequisites. Java Development Kit (JDK) is essential to run the product.
Install WSO2 Identity Server
- Download the latest version of WSO2 Identity Server.
- Extract the archive file to a dedicated directory for WSO2 Identity
Server, which will hereafter be referred to as
<IS_HOME>.
Set up JAVA_HOME
You must set your JAVA_HOME environment variable to
point to the directory where the Java Development Kit (JDK) is installed
on the computer.
Setting JAVA_HOME is a standard practice when you are using Java based programs. You may not need to do this manually depending on your Java Installer, as this variable is usually set by the Java installer itself. This guide is provided in case the JAVA_HOME variable has not been set or is incorrectly set on your machine.
Info
Environment variables are global system variables accessible by all the processes running under the operating system.
- In your home directory, open the BASHRC file in your favorite text editor, such as vi, emacs, pico, or mcedit.
-
Assuming you have JDK 1.8.0_141 in your system, add the following two lines at the bottom of the file, replacing
/usr/java/jdk-11.0.14with the actual directory where the JDK is installed.export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk-11.0.14 export PATH=${JAVA_HOME}/bin:${PATH} -
Save the file.
Info
If you do not know how to work with text editors in an SSH session, run the following command.
Paste the string from the clipboard and press "Ctrl+D".cat >> .bashrc -
If
JAVA_HOMEvariable is set correctly, following command will return the JDK installation path.echo $JAVA_HOME
Set system properties
If you need to set additional system properties when the server starts, you can take the following approaches:
- Set the properties from a script : Setting your system properties in the startup script is ideal, because it ensures that you set the properties every time you start the server. To avoid having to modify the script each time you upgrade, create your own startup script that wraps the WSO2 startup script and add the properties you want to set, rather than editing the WSO2 startup script directly.
- Set the properties from an external registry : If you want to access properties from an external registry, you could create Java code that reads the properties at runtime from that registry. Be sure to store sensitive data such as username and password to connect to the registry in a properties file instead of in the Java code and secure the properties file with the cipher tool.
You are now ready to run the product.
Install on Windows¶
Follow the instructions below to install the WSO2 Identity Server on Windows.
Install the required applications
- Ensure that your system meets the requirements specified in the Installation Prerequisites. Java Development Kit (JDK) is essential to run the product.
- Ensure that the
PATHenvironment variable is set toC:\Windows\System32, because thefindstrWindows.exe file is stored in this path.
Install WSO2 Identity Server
- Download the latest version of WSO2 Identity Server.
-
Extract the archive file to a dedicated directory for WSO2 Identity Server, which will hereafter be referred to as
<IS_HOME>. -
Set the
CARBON_HOMEenvironment variable by pointing it to the directory where you download WSO2 Identity Server into. For more information on how to do this, see here.
Set up JAVA_HOME
You must set your JAVA_HOME environment variable to
point to the directory where the Java Development Kit (JDK) is installed
on the computer. Typically, the JDK is installed in a directory under
C:/Program Files/Java, such as
C:/Program Files/Java/jdk-11.0.14 . If you have
multiple versions installed, choose the latest one, which you can find
by sorting by date.
Info
Environment variables are global system variables accessible by all the processes running under the operating system. You can define an environment variable as a system variable, which applies to all users, or as a user variable, which applies only to the user who is currently logged in.
You set up JAVA_HOME using the System Properties, as described below.
Alternatively, if you just want to set JAVA_HOME temporarily for the
current command prompt window, set it at the command
prompt.
Set up JAVA_HOME using the system properties
-
Right-click the My Computer icon on the desktop and choose Properties.
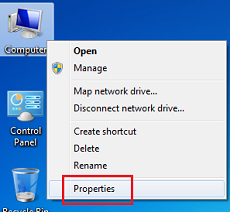
-
In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, and then click the Environment Variables button.
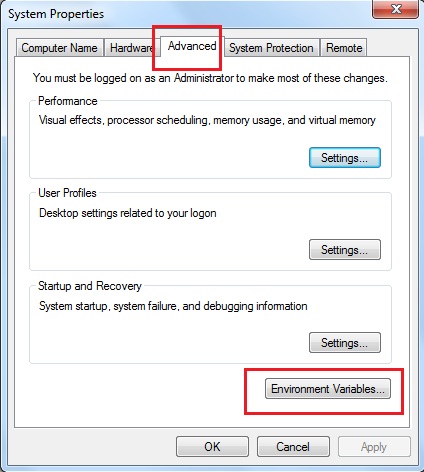
-
Click the New button under System variables (for all users) or under User variables (just for the user who is currently logged in).
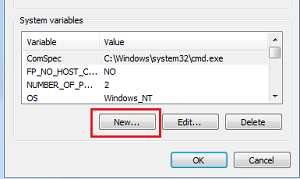
-
Enter the following information:
- In the Variable name field, enter:
JAVA_HOME - In the Variable value field, enter the installation path of
the Java Development Kit, such as:
c:/Program Files/Javajdk-11.0.14
- In the Variable name field, enter:
The JAVA_HOME variable is now set and will apply to any subsequent
command prompt windows you open. If you have existing command prompt
windows running, you must close and reopen them for the JAVA_HOME
variable to take effect, or manually set the JAVA_HOME variable in
those command prompt windows as described in the next section. To verify
that the JAVA_HOME variable is set correctly, open a
command window (from the Start menu, click Run, and then type
CMD and click Enter ) and execute the following
command.
set JAVA_HOMEThe system returns the JDK installation path. You are now ready to run the product.
Set JAVA_HOME temporarily using the Windows command prompt (CMD)
You can temporarily set the JAVA_HOME environment
variable within a Windows command prompt window (CMD). This is useful
when you have an existing command prompt window running and you do not
want to restart it.
-
In the command prompt window, enter the following command where
<JDK_INSTALLATION_PATH>is the JDK installation directory and press Enter.Format
set JAVA_HOME=<JDK_INSTALLATION_PATH>
Example
set JAVA_HOME=c:/Program Files/java/jdk-11.0.14The `JAVA_HOME variable is now set for the current CMD session only.
-
To verify that the
JAVA_HOMEvariable is set correctly, execute the following command:set JAVA_HOME -
The system returns the JDK installation path.
Set system properties
If you need to set additional system properties when the server starts, you can take the following approaches:
- Set the properties from a script : Setting your system properties in the startup script is ideal, because it ensures that you set the properties every time you start the server. To avoid having to modify the script each time you upgrade, create your own startup script that wraps the WSO2 startup script and add the properties you want to set, rather than editing the WSO2 startup script directly.
- Set the properties from an external registry : If you want to access properties from an external registry, you could create Java code that reads the properties at runtime from that registry. Be sure to store sensitive data such as username and password to connect to the registry in a properties file instead of in the Java code and secure the properties file with the cipher tool.
You are now ready to run the product.
Install as a Linux Service¶
WSO2 Carbon and any Carbon-based product can be run as a Linux service as described in the following sections:
Prerequisites
Install JDK and set up the JAVA_HOME environment variable. For more information,
see Installation Prerequisites.
Set up CARBON_HOME
Extract the WSO2 product that you want to run as a Linux service and set the environment
variable CARBON_HOME to the extracted product directory location.
Run the product as a Linux service
-
To run the product as a service, create a startup script and add it to the boot sequence. The basic structure of the startup script has three parts (i.e., start, stop and restart) as follows:
#!/bin/bash case "$1″ in start) echo "Starting Service" ;; stop) echo "Stopping Service" ;; restart) echo "Restarting Service" ;; *) echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart}" exit 1 esacClick to view an example startup script written for WSO2 Identity Server 6.1.0
#! /bin/sh ### BEGIN INIT INFO # Provides: wso2is # Required-Start: $all # Required-Stop: # Default-Start: 2 3 4 5 # Default-Stop: # Short-Description: starts the wso2 identity server ### END INIT INFO export JAVA_HOME="/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64" export CARBON_HOME="/home/ubuntu/wso2is-6.1.0" startcmd="${CARBON_HOME}""/bin/wso2server.sh start > /dev/null &" restartcmd="${CARBON_HOME}""/bin/wso2server.sh restart > /dev/null &" stopcmd="${CARBON_HOME}""/bin/wso2server.sh stop > /dev/null &" case "$1" in start) echo "Starting WSO2 Identity Server ..." su -c "${startcmd}" user1 ;; restart) echo "Re-starting WSO2 Identity Server ..." su -c "${restartcmd}" user1 ;; stop) echo "Stopping WSO2 Identity Server ..." su -c "${stopcmd}" user1 ;; *) echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart}" exit 1 esacIn the above script, the server is started as a user by the name user1 rather than the root user. I.e.,
su -c "${startcmd}" user1. -
Add the script to
/etc/init.d/folder and make it executable.Info
If you want to keep the scripts in a location other than
/etc/init.d/folder, you can add a symbolic link to the script in/etc/init.d/and keep the actual script in a separate location. Say your script name isidentityserverand it is in/opt/WSO2/folder, then the commands for adding a link to/etc/init.d/is as follows:-
Make your script executable:
sudo chmod a+x /opt/WSO2/identityserver -
Add a link to
/etc/init.d/:sudo ln -snf /opt/WSO2/identityserver /etc/init.d/identityserver
-
-
Install the startup script to respective runlevels using the command
update-rc.d. Following command is given for the sample script shown in step 1.sudo update-rc.d identityserver defaultsThe
defaultsoption in the above command makes the service to start in runlevels 2,3,4 and 5 and to stop in runlevels 0,1 and 6.Info
A runlevel is a mode of operation in Linux (or any Unix-style operating system). There are several runlevels in a Linux server and each of these runlevels is represented by a single digit integer. Each runlevel designates a different system configuration and allows access to a different combination of processes.
-
You can now start, stop and restart the server using
service <service name> {start|stop|restart}command.
Install as a Windows Service¶
Any Java-based application, including WSO2 Carbon and Carbon-based products, can be run as a Windows service by using a bridging tool such as Yet Another Java Service Wrapper (YAJSW).
Info
As YAJSW is distributed under the LGPL license and WSO2 is distributed under the Apache2 license, these two cannot be packed together in a distribution. However, any end-user or customer can freely combine components under these two licenses as long as the combined work is not distributed. The following instructions will guide you on the process of using YAJSW to install WSO2 Identity Server as a Windows Service.
Follow the instructions in the sections below to set it up.
Prerequisites
- Install JDK and set up the
JAVA_HOMEenvironment variable. For more information, see Installation Prerequisites. - Download and install a service wrapper library for running WSO2 Identity Server as a
Windows service. WSO2 recommends Yet Another Java Service Wrapper
(YAJSW ) version 13.03, and several WSO2 products
provide a default
wrapper.conffile in their<PRODUCT_HOME>/bin/yajsw/directory. The following instructions describe how to set up this file.
Set up the YAJSW wrapper configuration file
wrapper.conf file is used for wrapping Java Applications by YAJSW. The wrapper.conf file found in the
<IS_HOME>/bin/yajsw/ directory holds the minimal configuration for running a WSO2 product as a Windows Service.
Copy the wrapper.conf file found in the <IS_HOME>/bin/yajsw/ directory and paste it in the
<YAJSW_HOME>/conf/ directory. A sample wrapper.conf file that is packed with the WSO2 product is given below.
Info
If you wish to set additional properties from an external registry at runtime, store sensitive information like usernames and passwords for connecting to the registry in a properties file, and secure it with the cipher tool.
Click to view a sample
#********************************************************************
# working directory
#********************************************************************
wrapper.working.dir=${carbon_home}/
# Java Main class.
# YAJSW: default is "org.rzo.yajsw.app.WrapperJVMMain"
# DO NOT SET THIS PROPERTY UNLESS YOU HAVE YOUR OWN IMPLEMENTATION
# wrapper.java.mainclass=
#********************************************************************
# tmp folder
# yajsw creates temporary files named in_.. out_.. err_.. jna..
# per default these are placed in jna.tmpdir.
# jna.tmpdir is set in setenv batch file to <yajsw>/tmp
#********************************************************************
wrapper.tmp.path = ${jna_tmpdir}
#********************************************************************
# Application main class or native executable
# One of the following properties MUST be defined
#********************************************************************
# Java Application main class
wrapper.java.app.mainclass=org.wso2.carbon.bootstrap.Bootstrap
# Log Level for console output. (See docs for log levels)
wrapper.console.loglevel=INFO
# Log file to use for wrapper output logging.
wrapper.logfile=${wrapper_home}\/log\/wrapper.log
# Format of output for the log file. (See docs for formats)
#wrapper.logfile.format=LPTM
# Log Level for log file output. (See docs for log levels)
#wrapper.logfile.loglevel=INFO
# Maximum size that the log file will be allowed to grow to before
# the log is rolled. Size is specified in bytes. The default value
# of 0, disables log rolling by size. May abbreviate with the 'k' (kB) or
# 'm' (mB) suffix. For example: 10m = 10 megabytes.
# If wrapper.logfile does not contain the string ROLLNUM it will be automatically added as suffix of the file name
wrapper.logfile.maxsize=10m
# Maximum number of rolled log files which will be allowed before old
# files are deleted. The default value of 0 implies no limit.
wrapper.logfile.maxfiles=10
# Title to use when running as a console
wrapper.console.title=WSO2 Carbon
#********************************************************************
# Wrapper Windows Service and Posix Daemon Properties
#********************************************************************
# Name of the service
wrapper.ntservice.name=WSO2CARBON
# Display name of the service
wrapper.ntservice.displayname=WSO2 Carbon
# Description of the service
wrapper.ntservice.description=Carbon Kernel
#********************************************************************
# Wrapper System Tray Properties
#********************************************************************
# enable system tray
wrapper.tray = true
# TCP/IP port. If none is defined multicast discovery is used to find the port
# Set the port in case multicast is not possible.
wrapper.tray.port = 15002
#********************************************************************
# Exit Code Properties
# Restart on non zero exit code
#********************************************************************
wrapper.on_exit.0=SHUTDOWN
wrapper.on_exit.default=RESTART
#********************************************************************
# Trigger actions on console output
#********************************************************************
# On Exception show message in system tray
wrapper.filter.trigger.0=Exception
wrapper.filter.script.0=${wrapper_home}/scripts/trayMessage.gv
wrapper.filter.script.0.args=Exception
#********************************************************************
# genConfig: further Properties generated by genConfig
#********************************************************************
placeHolderSoGenPropsComeHere=
wrapper.java.command = ${java.home}/bin/java
wrapper.java.classpath.1 = ${carbon_home}/bin/*.jar
wrapper.java.classpath.2 = ${carbon_home}/lib/commons-lang-*.jar
wrapper.java.classpath.3 = ${carbon_home}/lib/*.jar
wrapper.app.parameter.1 = org.wso2.carbon.bootstrap.Bootstrap
wrapper.app.parameter.2 = RUN
wrapper.java.additional.1 = -Xbootclasspath/a:${carbon_home}/lib/xboot/*.jar
wrapper.java.additional.2 = -Xms256m
wrapper.java.additional.3 = -Xmx1024m
wrapper.java.additional.5 = -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError
wrapper.java.additional.6 = -XX:HeapDumpPath=${carbon_home}/repository/logs/heap-dump.hprof
wrapper.java.additional.7 = -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote
wrapper.java.additional.8 = -Dcarbon.registry.root=\/
wrapper.java.additional.9 = -Dcarbon.home=${carbon_home}
wrapper.java.additional.10 = -Dwso2.server.standalone=true
wrapper.java.additional.11 = -Djava.command=${java_home}/bin/java
wrapper.java.additional.12 = -Djava.io.tmpdir=${carbon_home}/tmp
wrapper.java.additional.13 = -Dcatalina.base=${carbon_home}/lib/tomcat
wrapper.java.additional.14 = -Djava.util.logging.config.file=${carbon_home}/repository/conf/etc/logging-bridge.properties
wrapper.java.additional.15 = -Dcarbon.config.dir.path=${carbon_home}/repository/conf
wrapper.java.additional.16 = -Dcarbon.logs.path=${carbon_home}/repository/logs
wrapper.java.additional.17 = -Dcomponents.repo=${carbon_home}/repository/components
wrapper.java.additional.18 = -Dconf.location=${carbon_home}/repository/conf
wrapper.java.additional.19 = -Dcom.atomikos.icatch.file=${carbon_home}/lib/transactions.properties
wrapper.java.additional.20 = -Dcom.atomikos.icatch.hide_init_file_path=true
wrapper.java.additional.21 = -Dorg.apache.jasper.runtime.BodyContentImpl.LIMIT_BUFFER=true
wrapper.java.additional.22 = -Dcom.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool.authentication=simple
wrapper.java.additional.23 = -Dcom.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool.timeout=3000
wrapper.java.additional.24 = -Dorg.terracotta.quartz.skipUpdateCheck=true
wrapper.java.additional.25 = -Dorg.apache.jasper.compiler.Parser.STRICT_QUOTE_ESCAPING=false
wrapper.java.additional.26 = -Dfile.encoding=UTF8
wrapper.java.additional.27 = -DworkerNode=false
wrapper.java.additional.28 = -Dhttpclient.hostnameVerifier=DefaultAndLocalhost
wrapper.java.additional.29 = -Dcarbon.new.config.dir.path=${carbon_home}/repository/resources/conf
wrapper.java.additional.30 = -Djava.util.logging.manager=org.apache.juli.ClassLoaderLogManagerInfo
If your JDK version is >= 11.0.20 or >= 17.0.8, you need to add the following two additional properties to the wrapper.conf file.
wrapper.java.additional.31 = -Djdk.util.zip.disableZip64ExtraFieldValidation=true
wrapper.java.additional.32 = -Djdk.nio.zipfs.allowDotZipEntry=trueSet up carbon_home
Extract the Carbon-based product that you want to run as a Windows
service, and then set the Windows environment variable carbon_home
to the directory that you extracted the product. For example, if you want to
run WSO2 IS 6.1.0 as a Windows service, you would set carbon_home to the
extracted wso2is-6.1.0 directory.
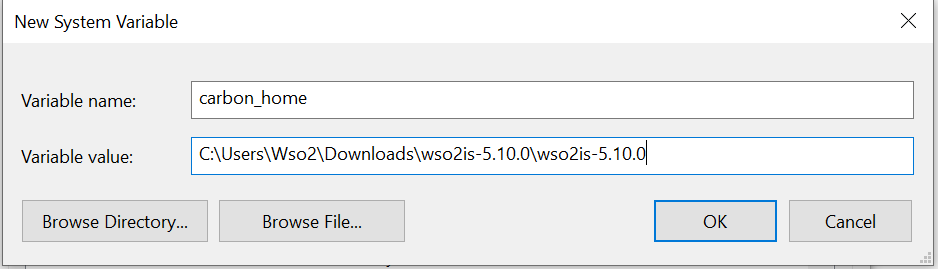
Run the product in console mode
You will now verify that YAJSW is configured correctly for running the Carbon-based product as a Windows service.
-
Open a Windows command prompt and go to the
<YAJSW_HOME>/bat/directory. For example:cd C:\Documents and Settings\yajsw_home\bat -
Start the wrapper in console mode using the following command:
runConsole.batIf the configurations are set properly for YAJSW, you will see console output similar to the following. Now you can access the WSO2 management console from your web browser via https://localhost:9443/carbon.
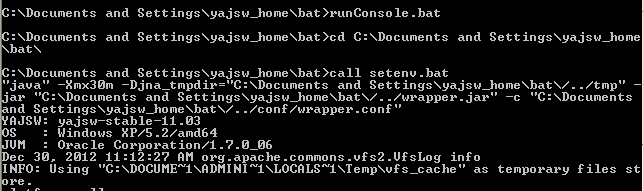
Work with the WSO2CARBON service
To install the Carbon-based product as a Windows service, open a console with administrative privileges and execute the
following command in the <YAJSW_HOME>/bat/ directory:
installService.batThe console will display a message confirming that the WSO2CARBON service has been installed.
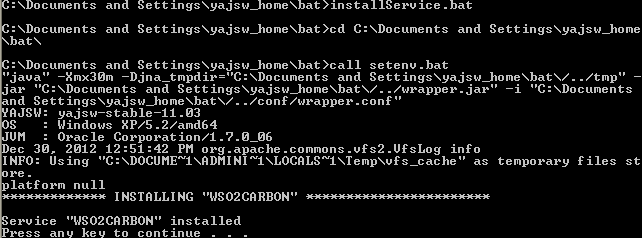
To start the service, execute the following command in the same console window (with administrative privileges):
startService.batThe console will display a message confirming that the WSO2CARBON service has been started.
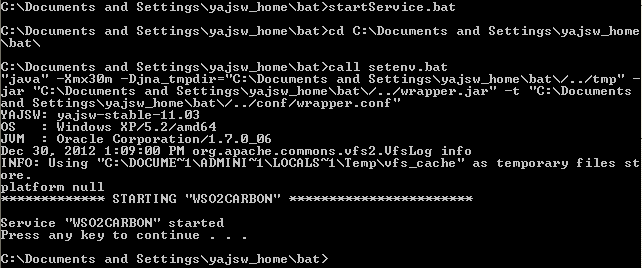
To stop the service, execute the following command in the same console window (with administrative privileges):
stopService.batThe console will display a message confirming that the WSO2CARBON service has been stopped.
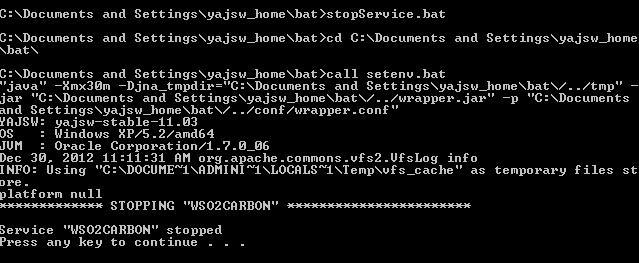
To uninstall the service, execute the following command in the same console window (with administrative privileges):
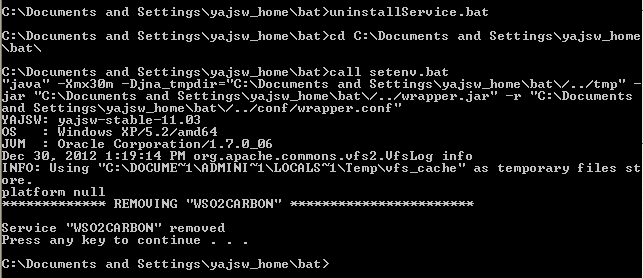
uninstallService.batThe console will display a message confirming that the WSO2CARBON service has been removed.
Uninstall the product¶
To remove an installed product, follow the instructions below:
| OS | Instructions |
|---|---|
| Mac OS | Open a terminal and run the following command as the root user: |
| Windows |
C:/Program
Files/WSO2/<PRODUCT_NAME>/<VERSION> |
| Ubuntu | Open a terminal and run the following command: |
| CentOS | Open a terminal and run the following command: |