Using the Configuration Management REST APIs¶
The configuration management APIs in WSO2 Identity Server manages configurations that are required to be stored as tenant-wise key-pair values. These stored configuration values are not changed frequently and are consumed at runtime. Some examples of such values are:
- SMTP configurations of an email server
- A server configuration where analytics data is published
Configurations for the above scenarios can be stored using the configuration management APIs. A detailed example is included in the try-it-out section below.
Prerequisites¶
Prior to using this REST API, ensure that the following requirements are met.
-
Execute the following DB scripts on the data source that is defined in the
identity.xmlfile found in the<IS_HOME>/repository/conf/identityfolder.
For more information about data sources, see Setting Up Separate Databases for Clustering .Tip
Note that this REST API has been tested only with H2 and MySQL5.7 databases.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS IDN_CONFIG_TYPE ( ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, DESCRIPTION VARCHAR(1023) NULL, PRIMARY KEY (ID), CONSTRAINT TYPE_NAME_CONSTRAINT UNIQUE (NAME) ); CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS IDN_CONFIG_RESOURCE ( ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, TENANT_ID INT NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, CREATED_TIME TIMESTAMP NOT NULL, LAST_MODIFIED TIMESTAMP NOT NULL, HAS_FILE BOOLEAN(1) NOT NULL, HAS_ATTRIBUTE BOOLEAN(1) NOT NULL, TYPE_ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, UNIQUE (NAME, TENANT_ID, TYPE_ID), PRIMARY KEY (ID) ); ALTER TABLE IDN_CONFIG_RESOURCE ADD CONSTRAINT TYPE_ID_FOREIGN_CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (TYPE_ID) REFERENCES IDN_CONFIG_TYPE (ID) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS IDN_CONFIG_ATTRIBUTE ( ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, RESOURCE_ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, ATTR_KEY VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, ATTR_VALUE VARCHAR(1023) NULL, PRIMARY KEY (ID), UNIQUE (RESOURCE_ID, ATTR_KEY, ATTR_VALUE) ); ALTER TABLE IDN_CONFIG_ATTRIBUTE ADD CONSTRAINT RESOURCE_ID_ATTRIBUTE_FOREIGN_CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (RESOURCE_ID) REFERENCES IDN_CONFIG_RESOURCE (ID) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS IDN_CONFIG_FILE ( ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, VALUE BLOB NULL, RESOURCE_ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR(255) NULL, PRIMARY KEY (ID) ); ALTER TABLE IDN_CONFIG_FILE ADD CONSTRAINT RESOURCE_ID_FILE_FOREIGN_CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (RESOURCE_ID) REFERENCES IDN_CONFIG_RESOURCE (ID) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE;CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS IDN_CONFIG_TYPE ( ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, DESCRIPTION VARCHAR(1023) NULL, PRIMARY KEY (ID), CONSTRAINT TYPE_NAME_CONSTRAINT UNIQUE (NAME) ); CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS IDN_CONFIG_RESOURCE ( ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, TENANT_ID INT NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, CREATED_TIME TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LAST_MODIFIED TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, HAS_FILE tinyint(1) NOT NULL, HAS_ATTRIBUTE tinyint(1) NOT NULL, TYPE_ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (ID), CONSTRAINT NAME_TENANT_TYPE_CONSTRAINT UNIQUE (NAME,TENANT_ID,TYPE_ID) ); ALTER TABLE IDN_CONFIG_RESOURCE ADD CONSTRAINT TYPE_ID_FOREIGN_CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (TYPE_ID) REFERENCES IDN_CONFIG_TYPE (ID) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS IDN_CONFIG_ATTRIBUTE ( ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, RESOURCE_ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, ATTR_KEY VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, ATTR_VALUE VARCHAR(1023) NULL, PRIMARY KEY (ID), CONSTRAINT RESOURCE_KEY_VAL_CONSTRAINT UNIQUE (RESOURCE_ID(64), ATTR_KEY(255)) ); ALTER TABLE IDN_CONFIG_ATTRIBUTE ADD CONSTRAINT RESOURCE_ID_ATTRIBUTE_FOREIGN_CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (RESOURCE_ID) REFERENCES IDN_CONFIG_RESOURCE (ID) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS IDN_CONFIG_FILE ( ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, VALUE BLOB NULL, RESOURCE_ID VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR(255) NULL, PRIMARY KEY (ID) ); ALTER TABLE IDN_CONFIG_FILE ADD CONSTRAINT RESOURCE_ID_FILE_FOREIGN_CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (RESOURCE_ID) REFERENCES IDN_CONFIG_RESOURCE (ID) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; -
The configuration management API sometimes uses dynamic query build for its database CRUD operations; especially in the
/searchendpoint (for more information, see Configuration Management REST APIs ). However, a query that is too long can lead to errors. To prevent this, an upper limit to the dynamic query size is applied by default (the default value is the maximum packet size for MySQL 5.7 in bytes). To configure this upper limit value, do the following:-
Add the following configuration to the
<IS_HOME>/repository/conf/deployment.tomlfile.[configuration.store.query_length] max="4194304
-
Configuration management architecture¶
The configuration manager exposed with the configuration management REST APIs manages configurations as Resources.
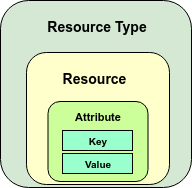
What is a resource?
- A Resource belongs to a Resource Type and a tenant domain.
- Each Resource has a set of Attributes.
- Each Attribute has a key and a respective value.
The section below describes each concept in more detail.
Configuration management concepts¶
-
Resource - A resource contains one or more attributes which will be used to store resource data. A resource is created in the tenant domain and it belongs to the authenticated user who creates the resource. When creating the resource, it is mandatory to assign a resource type.
-
Resource Type -
A resource type is shared among the tenants. Each resource created in a tenant domain, belongs to an already created resource type. Deleting a resource type will also delete its resources.Tip
Since the resource type is shared among tenants, deleting a resource type can affect resources in different tenant domains.
-
Attribute -
An attribute is the element that stores the data for its resource. An attribute is created for an already existing resource. It contains a key and a value.
APIs and supported operations¶
Note
For information on the REST APIs, supported operations and sample requests/responses, see Configuration Management APIs Documentation.
For information on how to use the /search endpoint of the Configuration Management APIs, see Retrieving Tenant Resources Based on Search Parameters.
Try it out¶
This section guides you through a sample scenario using the WSO2 IS configuration manager.
Sample scenario - Consider a scenario where you need to store the SMTP email configurations. Assume that the simple SMTP configuration has only one property.
| Property | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| From | "[email protected]" | This email address is used by the WSO2 IS instance to send an email. |
To store the SMTP email configuration, follow the steps given below:
- Start WSO2 Identity Server and access the management
console. You can sign in using
adminas the username and password. -
Open a terminal window and run the following commands.
-
Create a resource type named "email" using the Create resource type API.
Sample Request
curl -k -X POST https://localhost:9443/api/identity/config-mgt/v1.0/resource-type -H "accept: application/json" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -H 'Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=' -d '{"name": "e-mail", "description": "This is the resource type for email resources."}'Sample Response
{"name":"e-mail","id":"0adbdfad-5f4f-4c11-af75-9ed3e93647b9","description":"This is the resource type for email resources."} -
Create a resource named "smtp" in the super tenant domain under the "email" resource type using the Create resource API. Note that the "from" attribute is defined within this sample request therefore, when the new resource is created a new attribute named "from" will be created under the "smtp" resource as well.
Sample Request
curl -k -X POST https://localhost:9443/api/identity/config-mgt/v1.0/resource/e-mail -H "accept: application/json" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -H 'Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=' -d '{"name": "smtp","attributes": [{"key": "from","value": "[email protected]"}]}'Sample Response
{"resourceId":"6e45c661-7671-4ee9-805c-8d3d1df46cbc","tenantDomain":"carbon.super","resourceName":"smtp","resourceType":"e-mail","lastModified":"2019-02-07T09:30:12.963Z","created":"2019-02-07T09:30:12.963Z","attributes":[{"key":"from","value":"[email protected]"}],"files":[]}
-
-
Next, assume that you now need to add an additional attribute named "to" to the "smtp" email configuration. To do this, create a new attribute named "to" using the Create attribute API by running the following command on the terminal.
Sample Request
curl -k -X POST https://localhost:9443/api/identity/config-mgt/v1.0/resource/e-mail/smtp -H "accept: application/json" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -H 'Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=' -d '{"key": "to", "value": "abc.com"}'Sample Response
{"key":"to","value":"abc.com"} -
Once these steps are completed, the WSO2 IS instance calls the configuration manager to retrieve the SMTP email address using the following path:
(Resource Type = ‘e-mail’) -> (Resource = ‘smtp’) -> (Attribute key = ‘from’)Run the following curl command to retrieve the 'smtp' resource that you created above.
Sample Request
curl -k -X GET https://localhost:9443/api/identity/config-mgt/v1.0/resource/e-mail/smtp -H "accept: application/json" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -H 'Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4='Sample Response
{"resourceId":"6e45c661-7671-4ee9-805c-8d3d1df46cbc","tenantDomain":"carbon.super","resourceName":"smtp","resourceType":"e-mail","lastModified":"2019-02-07T09:31:21.564Z","created":"2019-02-07T09:30:12.963Z","attributes":[{"key":"from","value":"[email protected]"},{"key":"to","value":"abc.com"}],"files":[]}