Configuring Multi-factor Authentication using FIDO¶
This section provides details on Fast IDentity Online (FIDO) and instructions on how to configure multi-factor authentication (MFA) in WSO2 Identity Server using FIDO.
Info
For information on MFA concepts, see About MFA.
Before you Begin
Certain changes made to the chrome u2f extension are causing the FIDO device to not register properly as an authentication factor. Additionally, Firefox no longer supports the u2f extension. WSO2 Identity Server resolves this by using the WebAuthn API to enable FIDO-based authentication. The WebAuthn API is already supported by the following browser versions:
- Chrome(CHROME 67)
- Firefox (FIREFOX 60)
- Edge (EDGE 17723)
To define the set of origin URLs where the WSO2 Identity Server Dashboard will be hosted (e.g., https://localhost:9443):
- Open the
deployment.tomlfile in the<IS_HOME>/repository/confdirectory. - Add the following configuration.
[fido.trusted] origins=["https://localhost:9443"]
About FIDO¶
FIDO attempts to change the nature of authentication by developing specifications that define an open, scalable, interoperable set of mechanisms that supplant reliance on passwords to securely authenticate users of online services. In short, FIDO Universal Second Factor (FIDO U2F) can make it easy for you to authenticate users while also ensuring that security is enhanced.
FIDO provides two user experiences to address a wide range of use cases and deployment scenarios. FIDO protocols are based on public key cryptography and are strongly resistant to phishing.
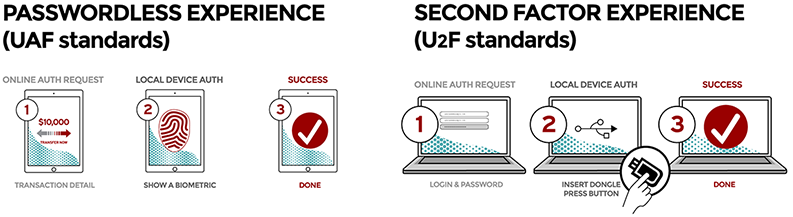
UAF¶
Universal Authentication Framework (UAF) involves a passwordless experience with the following key processes:
- The user carries the client device with the UAF stack installed.
- The user presents a local biometric or PIN.
- The website can choose whether to retain the password.
U2F¶
U2F focuses on the second factor experience and has the following key processes:
- The user carries the U2F device with built-in support in web browsers.
- The user presents the U2F device.
- The website can simplify the password (for example, it can be simplified to a 4-digit PIN).
U2F tokens provide cryptographic assertions that can be verified by relying parties. Typically, the relying party is a web server, and the cryptographic assertions are used as the second factor (in addition to passwords) during user authentication. U2F tokens are typically small special-purpose devices and FIDO Client is a web browser that communicates between the token and relying party.
Operations¶
The following are the two main operations that take place when using FIDO U2F.
- Registration: Upon registration, a device gives the server its attestation certificate. This certificate can be (optionally) used to verify the authenticity of the device.
- Authentication: The authentication operation proves possession of a previously-registered keypair to the relying party.
Phases¶
Both the registration and authentication operations consist of three phases depicted in the following figure.
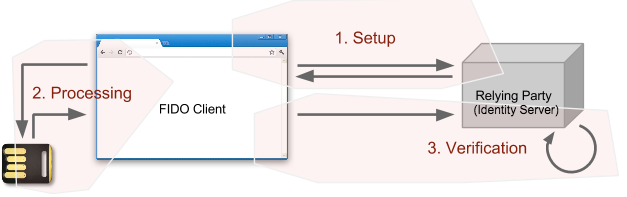
- Setup: In this phase, the FIDO Client contacts the relying party and obtains a challenge. Using the challenge (and possibly other data obtained from the relying party and/or prepared by the FIDO Client itself), the FIDO Client prepares a request message for the U2F Token.
- Processing: In this phase, the FIDO Client sends the request message to the token, and the token performs some cryptographic operations on the message, creating a response message. This response message is sent to the FIDO Client.
- Verification : In this phase, the FIDO Client transmits the token's response message, along with other data necessary for the relying party to verify the token response, to the relying party. The relying party then processes the token response and verifies its accuracy. A correct registration response will cause the relying party to register a new public key for a user, while a correct authentication response will cause the relying party to accept that the client is in possession of the corresponding private key.
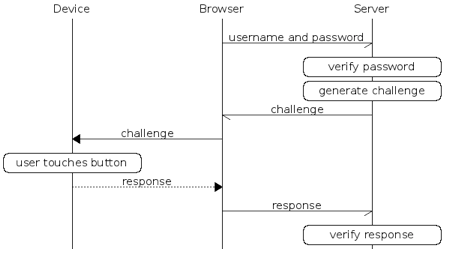
Authentication flow¶
The following depicts the FIDO U2F-based authentication process.
Info
For information on FIDO alliance, see What is FIDO.
Configuring MFA using FIDO¶
The instructions in this section enable you to successfully set up MFA using the WSO2 Identity Server.
Warning
FIDO authenticator can be configured only after a local authenticator is configured in the previous steps. It cannot be configured as the first step or if federated authenticator set the subject identifier.
Before you begin
If you are using a reverse proxy enabled setup, configure the relevant server URL as the AppID.
[authentication.authenticator.fido.parameters]
AppID="https://hostname"Setting up an account for MFA¶
- Sign in to WSO2 Identity Server Dashboard.
- Navigate to the My Profile section by clicking the associated View Details button.
-
Plug the FIDO device that you need to add to your computer if you have not already added and click Manage U2F Authentication.
-
You can add a new U2F device to your account and remove it if needed. Too add the new U2F device,
- Click the Attach FIDO Token button.
- Touch the 'key' icon on the FIDO device. Note that the added device is listed in the next screen.
Tip
You can have multiple devices associated with your account.
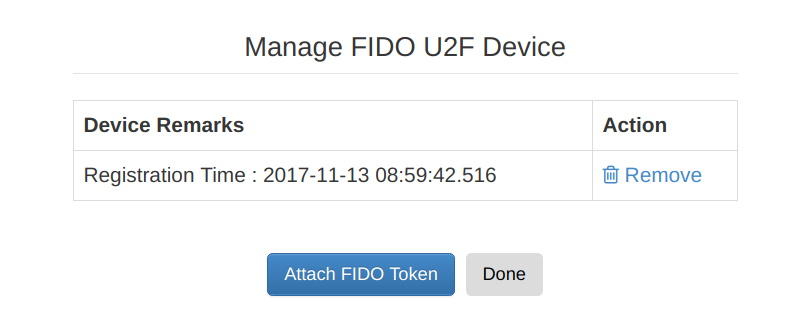
Configuring FIDO U2F as an authenticator¶
- Sign in to the Management Console.
-
To create a new Service Provider:
- On the Main menu, click Identity > Service Providers > Add.
- Enter a name and a brief description of the service provider.
- Click Register.
Info
For more information on creating a service provider, see Adding and Configuring a Service Provider.
-
In the Local & Outbound Authentication Configuration section, select Advanced Configuration.
Info
For more information on configuring the local and outbound authentication configuration, see Configuring Local and Outbound Authentication for a Service Provider .
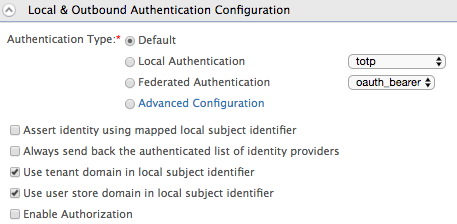
-
Under Local Authenticators section, click Add Authentication Step.
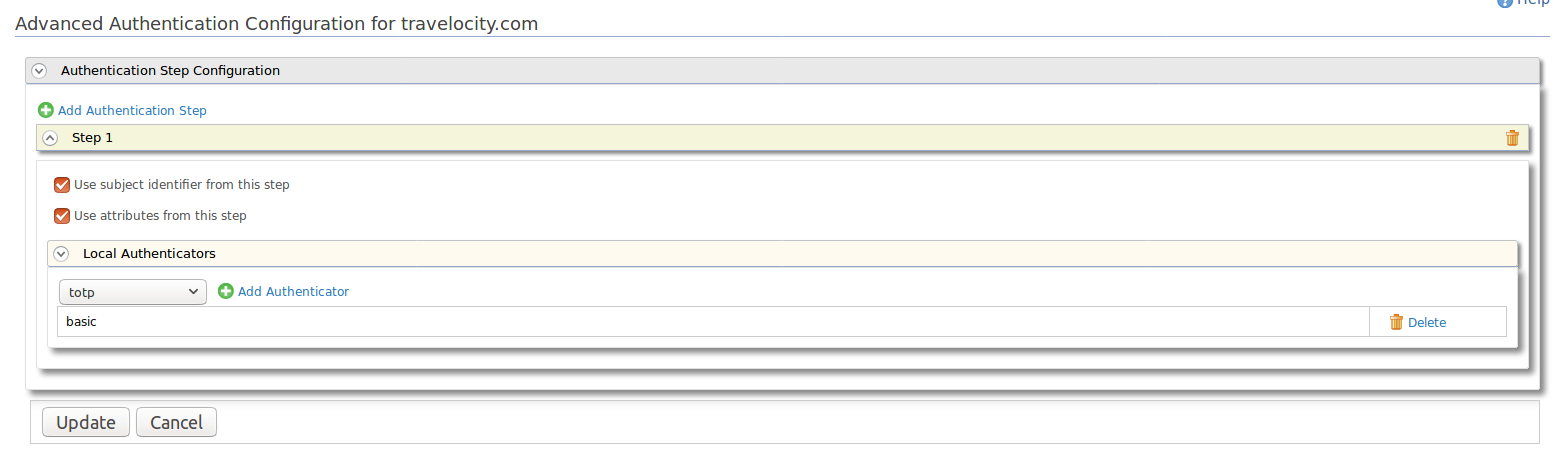
- Select Use subject identifier from this step and Use attributes from this step options.
- To add FIDO as the second-step authenticator, click Add Authentication step and add FIDO authenticator from Local Authenticators section.
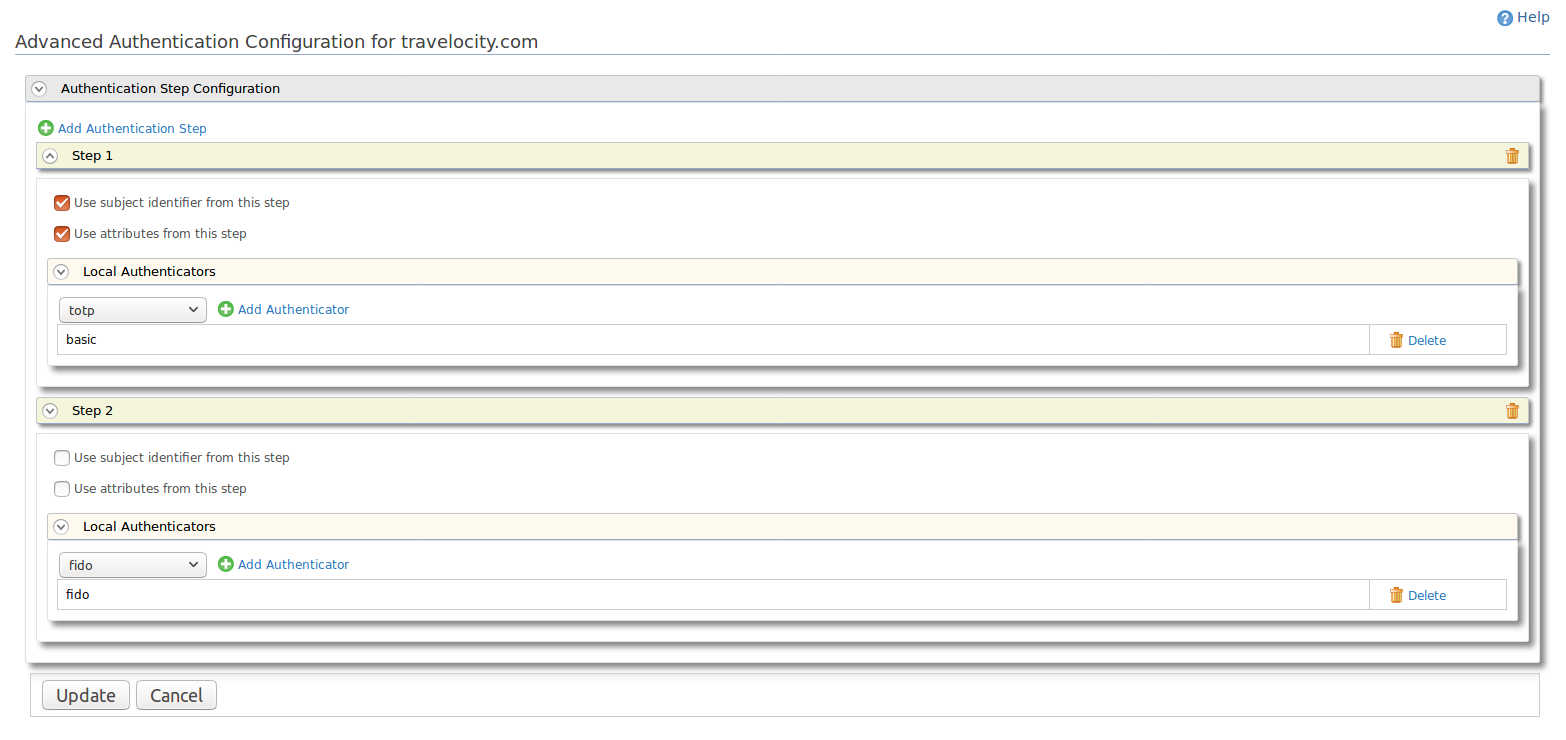
- Click the Update. Note that you will be redirected to the previous screen with the newly configured authentication steps.
Browser support for FIDO devices¶
The https://demo.yubico.com/u2f site can be used to check the browser support for FIDO devices.
As for now, Google Chrome (version 38 or later) has support for FIDO devices. Firefox does not support FIDO natively. An add-on must be added to Firefox to support FIDO devices. You can download and install the add-on from here.
Top