User Managed Access Endpoints¶
This section describes the different endpoints used by User Managed Access.
Resource registration endpoint¶
This endpoint allows the resource server to place resources under the protection of the authorization server on behalf of the resource owner. The resource server uses a RESTful API resource registration endpoint at the authorization server to create, read, update, and delete resource descriptions and list all resources. The resource description consists of JSON documents that are maintained as web resources. In the normal process, protection of a resource starts with successful registration and ends with successful deregistration.
Resource description¶
The figure below shows the flow of the request made by the resource server to the authorization server (01) and response generated by authorization server to the resource server (02).
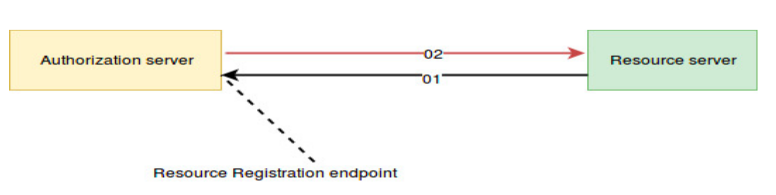
Resource description is a JSON object which explains the characteristics of the resource that is to be put under the protection of the authorization server.
Given below is an example of the resource description.
{
"resource_scopes":[
"view",
"http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/print"
],
"description":"Collection of digital photographs",
"icon_uri":"http://www.example.com/icons/flower.png",
"name":"Photo Album",
"type":"http://www.example.com/rsrcs/photoalbum"
}The resource description has the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description | Mandatory/Optional |
|---|---|---|
resource_scopes |
A plain string, a URI, or an array of strings which indicates the available scopes for the resource. | Mandatory |
name |
A human-readable string naming the resource. The authorization server can use the referenced icon in the user interface when presenting information to a resource owner. | Mandatory |
description |
A human-readable string describing the resource in detail. The authorization server can use this description in the user interface when presenting information to a resource owner. | Optional |
icon_uri |
A URI for a graphic icon representing the resource. The authorization server can use the referenced icon in the user interface when presenting information to a resource owner. | Optional |
type |
A string identifying the semantics of the resource. The authorization server can use this information when processing information about the resource or displaying information about it in the user interface when presenting information to a resource owner. | Optional |
Resource registration APIs¶
The authorization server must support the following five
registration options. You need a valid Protection API Access Token (PAT)
to access them. Here, resourceregistration stands for
the resource registration endpoint and _id stands for
the authorization server-assigned identifier for the web resource
corresponding to the resource at the time it was created, included
within the URL returned in the location header.
The following five operations can be performed from this endpoint:
| HTTP method | Description | URI |
|---|---|---|
POST |
Create the resource description. | resourceregistration/resource |
GET |
Read the resource description. | resourceregistration/resource/_id |
PUT |
Update the resource description. | resourceregistration/resource/_id |
DELETE |
Delete the resource description. | resourceregistration/resource/_id |
GET |
List the resource descriptions. | resourceregistration/ |
Error messages¶
When the request to the resource registration endpoint is incorrect, the authorization server responds as follows:
| Error Code | Description |
|---|---|
| HTTP 404 (Not Found) | If the referenced resource cannot be found, the authorization server must respond with an HTTP 404 status code and may respond with a |
| HTTP 405 (Method Not Allowed) | If the resource server request used an unsupported HTTP method, the authorization server must respond with the HTTP 405 status code and may respond with an |
| HTTP 400 (Bad Request) | If the request is missing a required parameter, includes an invalid parameter value, includes a parameter more than once, or is otherwise malformed, the authorization server must respond with the HTTP 400 status code and may respond with an |
Creating a resource description¶
The create resource operation adds a new resource to the authorization server using the POST method.
Request
POST : https://localhost:9443/api/identity/oauth2/uma/resourceregistration/v1.0/resource HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer 8ff019ba-4f8e-3ed9-9b13-a077d9d04557
...
{
"resource_scopes":[
"read-public",
"post-updates",
"read-private",
"http://www.example.com/scopes/all"
],
"icon_uri":"http://www.example.com/icons/photoAlbem.png",
"name":"PhotoAlbem",
"type":"http://www.example.com/rsrcs/socialstream/140-compatible"
}If the request is successful, the resource is registered in the
authorization server and the 201 (Created) status message which includes
a location header and a _id parameter is returned.
Response
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/json
Location: /resource/2292d2f5-df72-4c2e-a918-5ae18b900855
...
{
"_id":"2292d2f5-df72-4c2e-a918-5ae18b900855",
"user_access_policy_uri":"http://as.example.com/rs/222/resource/KX3A-39WE/policy"
}Reading a resource description¶
This operation reads the previously registered resource description using the GET method.
Request
GET: https://localhost:9443/api/identity/oauth2/uma/resourceregistration/v1.0/resource/2292d2f5-df72-4c2e-a918-5ae18b900855
HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json Authorization: Bearer 8ff019ba-4f8e-3ed9-9b13-a077d9d04557If the request is successful, the response returns the 200 (OK) status
message with a body that contains the referenced resource description
along with a _id parameter.
Response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
...
{
"_id":"2292d2f5-df72-4c2e-a918-5ae18b900855",
"resource_scopes":[
"read-public",
"post-updates",
"read-private",
"http://www.example.com/scopes/all"
],
"icon_uri":"http://www.example.com/icons/PhotoAlbem.png",
"name":"PhotoAlbem",
"type":"http://www.example.com/rsrcs/socialstream/140-compatible"
}Updating a resource description¶
This operation updates the resource description. It replaces the previous description with the new description using the PUT method.
Request
PUT : https://localhost:9443/api/identity/oauth2/uma/resourceregistration/v1.0/resource/
2292d2f5-df72-4c2e-a918-5ae18b900855 HTTP/1.1
HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer 8ff019ba-4f8e-3ed9-9b13-a077d9d04557
...
{
"resource_scopes":[
"http://photoz.example.com/dev/scopes/view",
"public-read"
],
"description":"Collection of digital photographs",
"icon_uri":"http://www.example.com/icons/nature.png",
"name":"Photo Album 90",
"type":"http://www.example.com/rsrcs/photoalbum90"
}If the request is successful, it returns 200 (OK) as the response from
the authorization server and it includes the _id
parameter.
Response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
...
{
"_id":"2292d2f5-df72-4c2e-a918-5ae18b900855"
}Deleting a resource description¶
This operation removed a previously registered resource and its information.
Request
DELETE : https://localhost:9443/api/identity/oauth2/uma/resourceregistration/v1.0/resource/
2292d2f5-df72-4c2e-a918-5ae18b900855
HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json Authorization: Bearer 8ff019ba-4f8e-3ed9-9b13-a077d9d04557If the request is successful, the authorization server responds with an HTTP 200 or 204 status message.
Response
HTTP/1.1 204 No content
...Listing a resource descriptions¶
This operation lists down all the resources of a specific resource owner using the GET method.
Request
GET : https://localhost:9443/api/identity/oauth2/uma/resourceregistration/v1.0/resource
Authorization: Bearer 204c69636b6c69
HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer 8ff019ba-4f8e-3ed9-9b13-a077d9d04557If the request is successful, a response in string array format is
returned.
Example:
Response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
...
[
"2292d2f5-df72-4c2e-a918-5ae18b900855",
"d163001d-e8ec-4b11-b89e-7c5d891e878e",
"3a62e677-4bd9-4dfb-87b6-c305ec17b339",
"763bc9cf-3753-44e8-ba86-389b9913f971"
]Permission endpoint¶
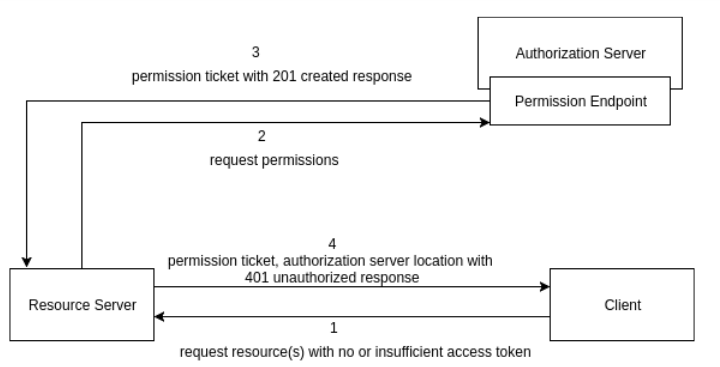
The permission endpoint of the authorization server is used by the resource server to request permissions on behalf of the client. This process is initiated when a client makes a tokenless resource request or a request with an invalid token to the resource server. The resource server interprets the request made to the client and maps it to the relevant authorization server, resource owner, resource identifiers, and their corresponding set of scopes. Note that in a single instance, the resource server can only request permission to access the resources of a single resource owner that is protected by a single authorization server. The resource server decides whether to request zero or more scopes corresponding to a resource identifier.
The diagram given below illustrates a request made to the permission endpoint with a success response in return.
Error messages¶
The error code can either be invalid_resource_id or
invalid_resource_scope .
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
Invalid_resource_id |
This indicates that the resource ID does not exist in the authorization server. |
Invalid_resource_scope |
This indicates that at least one of the scopes corresponding to the resource is not found at the authorization server. |
Creating a permission ticket¶
This creates a permission ticket using the POST HTTP method. A sample request made by the resource server to the authorization server is shown below:
Request
POST https://localhost:9443/api/identity/oauth2/uma/permission/v1.0/permission
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer 8ff019ba-4f8e-3ed9-9b13-a077d9d04557
...
[
{
"resource_id":"238157ba-06f4-4730-8492-86e35f5b2b7d",
"resource_scopes":[
"view",
"crop",
"lightbox"
]
},
{
"resource_id":"238157ba-06f4-4730-8492-86e35f8b2b32",
"resource_scopes":[
"view",
"layout",
"print"
]
},
{
"resource_id":"238157ba-06f4-8676-8492-86e35f5b2b7d",
"resource_scopes":[
"http://www.example.com/scopes/all"
]
}
]The Protection API Access Token (PAT) provided in the request header is used by the authorization server to identify the relevant resource owner and resource server. If the permission request is successful, then the authorization server sends a permission ticket in the success response as shown below:
Response
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/json
...
{
"ticket":"016f84e8-f9b9-11e0-bd6f-0021cc6004de"
}You would get a response similar to what is shown below, if the permission request is authenticated successfully, but fails due to some other reason.
Response
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Content-Type: application/json
...
{
"error":"invalid_resource_id",
"error_description":"Permission request failed with bad resource ID."
}