Configuring SAML 2.0 Web SSO¶
In a single sign on system there are two roles; Service Providers and Identity Providers. The important characteristic of a single sign on system is the pre-defined trust relationship between the service providers and the identity providers. Service providers trust the assertions issued by the identity providers and the identity providers issue assertions based on the results of authentication and authorization of principles which access services on the service provider's side.
SAML 2.0 web browser-based single-sign-on profile is defined under the SAML 2.0 Profiles specification. In a web browser-based SSO system, the flow can be started by the user either by attempting to access a service at the service provider, or by directly accessing the identity provider itself.
Preliminary Configs¶
Follow the steps below to navigate to the federated authenticators configuration section.
Before you begin
-
Sign in to the WSO2 Identity Server Management Console at
https://<SERVER_HOST>:9443/carbonas an administrator.
-
On the Main menu of the Management Console, click Identity > Identity Providers > Add.
Info
For more information on identity providers, see Adding and Configuring an Identity Provider.
-
Enter a suitable name for the identity provider in the Identity Provider Name text box.
-
Under the Federated Authenticators section, click SAML2 Web SSO Configuration.
-
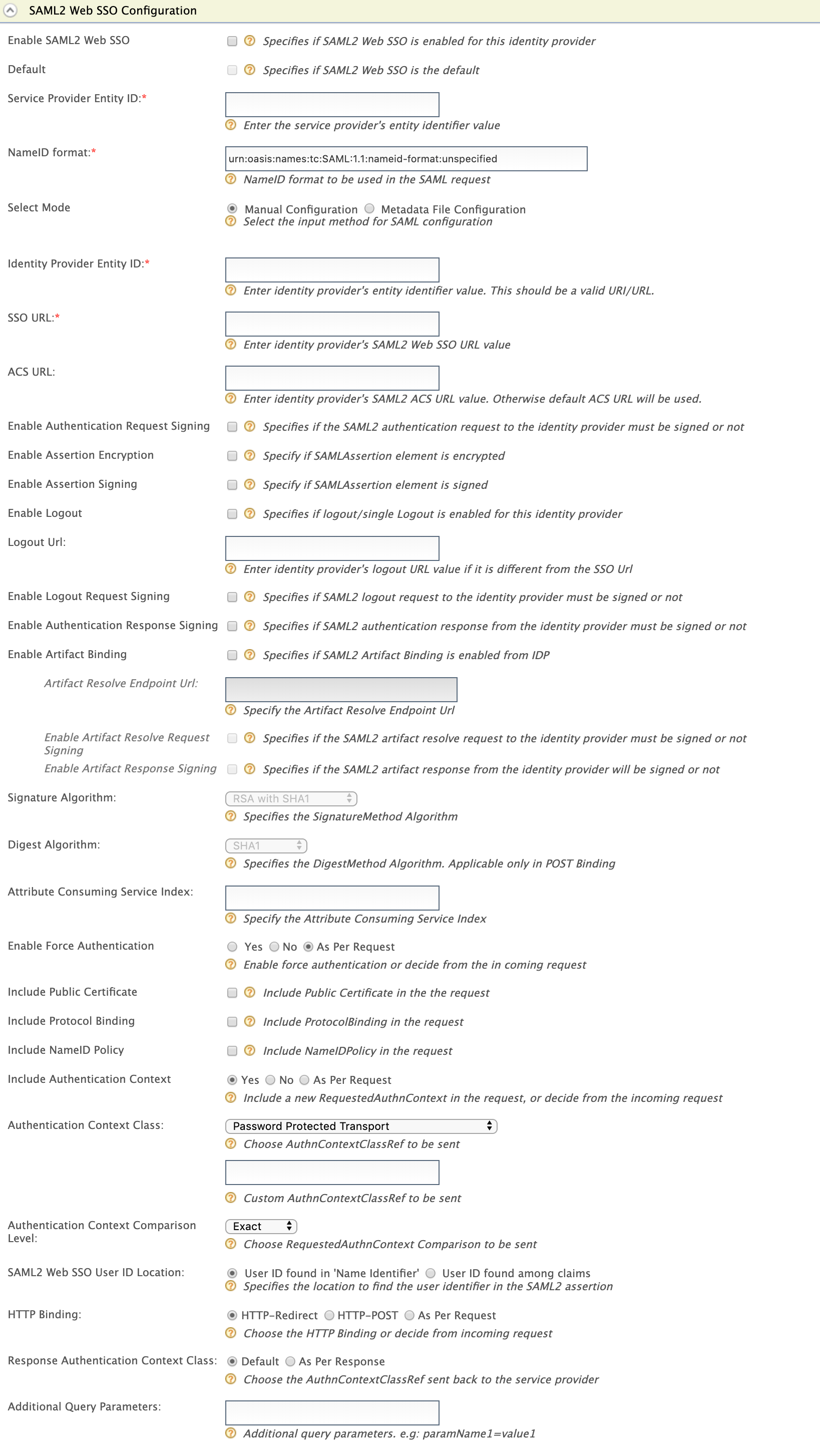
Enter the following values as given below.
Field Description Sample Value Enable SAML2 Web SSO Selecting this option enables SAML2 Web SSO to be used as an authenticator for users provisioned to the Identity Server. Selected Default Selecting the Default checkbox signifies that SAML2 Web SSO is the main/default form of authentication. This removes the selection made for any other Default checkboxes for other authenticators. Selected Service Provider Entity Id This is the entity Id of the Identity Server. This can be any value but when you configure a service provider in the external IDP you should give the same value as the Service Provider Entity Id.
wso2is
NameID format This is the NameID format to be used in the SAML request. By default, it has
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified. But you can change this as per the identity provider.urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecifiedYou proceed with the subsequent steps based on your preferred configuration mode.
Manual Configs¶
To configure manually,
-
Perform the preliminary configs.
-
Enter the required values as given below.
Field Description Sample Value
Select Mode Select the mode to decide the input method for SAML configuration. You can have manual configuration or Metadata data configuration where an .xml metadata file is uploaded. Manual configurationIdentity Provider Entity Id This is basically the <Issuer> value of the SAML2 response from the identity provider you are configuring. This value must be a unique string among identity providers inside the same tenant. This information should be taken from the external Identity provider.
In order to enable the <Issuer> validation in the SAML2 response from the IdP, open the
/repository/conf/deployment.toml https://idp.example.org/idp/shibboleth SSO URL This is the URL that you want to send the SAML request to. This information should be taken from the external Identity provider. https://localhost:8443/idp/profile/SAML2/Redirect/SSOACS URL This is the identity provider's SAML2 ACS URL.
Warning
To configure this, apply the 2020-01-17 WUM update to WSO2 Identity Server 5.9.0 using the WSO2 Update Manager (WUM).
To deploy a WUM update into production, you need to have a paid subscription. If you do not have a paid subscription, you can use this feature with the next version of WSO2 Identity Server when it is released. For more information on updating WSO2 Identity Server using WUM, see Getting Started with WUM in the WSO2 Administration Guide.
If not entered, the default ACS URL will be used. Enable Authentication Request Signing Selecting this checkbox enables you to sign the authentication request. If this is enabled, you must sign the request using the private key of the identity provider. Selected Enable Assertion Encryption This is a security feature where you can encrypt the SAML2 Assertions returned after authentication. So basically, the response must be encrypted when this is enabled. Selected Enable Assertion Signing Select Enable Assertion Signing to sign the SAML2 Assertions returned after the authentication. SAML2 relying party components expect these assertions to be signed by the Identity Server.
Selected Enable Logout Select Enable Single Logout so that all sessions are terminated once the user signs out from one server. Selected Logout URL If the external IDP support for logout you can select Enable Logout . Then you can set the URL of the external IDP, where you need to send the logout request, under Logout URL. If you do not set a value for this it will simply return to the SSO URL .https://localhost:8443/idp/samlsso/logout Enable Logout Request Signing Selecting this checkbox enables you to sign the logout request. Selected Enable Authentication Response Signing Select Enable Authentication Response Signing to sign the SAML2 responses returned after the authentication.
Selected Signature Algorithm Specifies the ‘SignatureMethod’ algorithm to be used in the ‘Signature’ element in POST binding and “SigAlg” HTTP Parameter in REDIRECT binding. The expandable Signature Algorithms table below lists the usable algorithms and their respective URIs that will be sent in the actual SAMLRequest.
Default value: RSA with SHA1Digest Algorithm Specifies the ‘DigestMethod’ algorithm to be used in the ‘Signature’ element in POST binding. The Digest Algorithms table below lists the usable algorithms and their respective URIs that will be sent in the actual SAMLRequest.
Default value: SHA1Attribute Consuming Service Index Specifies the ‘AttributeConsumingServiceIndex’ attribute. By default this would be empty, therefore that attribute would not be sent unless filled. Enable Force Authentication Enable force authentication or decide from the incoming request. This affects ‘ForceAuthn’ attribute. Default value: As Per RequestInclude Public Certificate Include the public certificate in the request. Selected by default Include Protocol Binding Include ‘ProtocolBinding’ attribute in the request. Selected by default Include NameID Policy Include ‘NameIDPolicy’ element in the request. Selecte d by default Include Authentication Context Include a new ‘RequestedAuthnContext’ element in the request, or reuse from the incoming request. Default value: YesAuthentication Context Class Choose an Authentication Context Class Reference (AuthnContextClassRef) to be included in the requested authentication context from the Identity Server which specifies the authentication context requirements of authentication statements returned in the response. Authentication Context Class table below lists the usable classes and their respective URIs that will be sent in the SAMLRequest from the Identity Server to trusted IdP.
Default value: PasswordProtectedTransport.Authentication Context Comparison Level Choose the Requested Authentication Context ‘Comparison’ attribute to be sent which specifies the comparison method used to evaluate the requested context classes or statements.
- If Comparison is set to "exact" or omitted, then the resulting authentication context in the authentication statement MUST be the exact match of at least one of the authentication contexts specified.
- If Comparison is set to "minimum", then the resulting authentication context in the authentication statement MUST be at least as strong (as deemed by the responder) as one of the authentication contexts specified.
- If Comparison is set to "better", then the resulting authentication context in the authentication statement MUST be stronger (as deemed by the responder) than any one of the authentication contexts specified.
- If Comparison is set to "maximum", then the resulting authentication context in the authentication statement MUST be as strong as possible (as deemed by the responder) without exceeding the strength of at least one of the authentication contexts specified.
Default value: ExactSAML2 Web SSO User Id Location Select whether the User ID is found in 'Name Identifier' or if it is found among claims. If the user ID is found amongthe claims, it can override the User ID Claim URI configuration in the identity provider claim mapping section . User ID found among claims HTTP Binding Select the HTTP binding details that are relevant for your scenario. This refers to how the request is sent to the identity provider. HTTP-Redirect and HTTP-POST are standard means of sending the request. If you select As Per Request it can handle any type of request. HTTP-POST Response Authentication Context Class Select As Per Response to pass the AuthnContextClassRefreceived from the configured identity provider to the service provider. Select Default to pass the defaultAuthnContextClassRefinstead.
TheAuthnContextClassRefspecifies how the user has been authenticated by the IdP (e.g. via username/password login, via certificate etc.)As Per Response Additional Query Parameters This is necessary if you are connecting to another Identity Server or application. Sometimes extra parameters are required by this IS or application so these can be specified here. These will be sent along with the SAML request.
Info
If you want to send query parameters that need to be updated dynamically with each SAML request, the value needs to be defined within parenthesis.This value should be the key of the query parameter sent in the SAML request URL.
Example:locale={lang}Multiple parameters can be defined by separation of query parameters using the
&character.Example:locale={lang}&scope=openid email profileparamName1=value1 -
Click Register.
Information on security algorithms
The following table lists out the security algorithms and their respective URI.
| Security algorithm name | Security algorithm URI |
|---|---|
| DSA with SHA1 | http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#dsasha1 |
| ECDSA with SHA1 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsigmore#ecdsasha1 dsasha1 |
| ECDSA with SHA256 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsigmore#ec dsasha256 |
| ECDSA with SHA384 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsigmore#ec dsasha384 |
| ECDSA with SHA512 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsigmore#ec dsasha512 |
| RSA with MD5 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsigmore#rsa md5 |
| RSA with RIPEMD160 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsigmore#rsa ripemd160 |
| RSA with SHA1 | http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#rsasha1 |
| RSA with SHA256 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsigmore#rsa sha256 |
| RSA with SHA384 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsigmore#rsa sha384 |
| RSA with SHA512 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsigmore#rsa sha512 |
Information on digest algorithms
The following table lists out the digest algorithms and their respective URI.
| Digest algorithm name | Digest algorithm URI |
|---|---|
| MD5 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsigmore#md 5 |
| RIPEMD160 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#ripemd16 0 |
| SHA1 | http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#sha1 |
| SHA256 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#sha256 |
| SHA384 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsigmore#sh a384 |
| SHA512 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#sha512 |
Information on authentication context classes
The following table lists out the authentication context classes and their respective URI.
File-Based Configs¶
About Metadata upload
When configuring a service provider (SP) or federated Identity Provider (Federated IdP), the user is required to enter configuration data to facilitate exchanging authentication and authorization data between entities in a standard way. Apart from manual entering of configuration data, the Identity Server 5.3.0 provides the facility to upload configuration data using a metadata xml file or referring to metadata xml file located in a predetermined URL. These two methods of uploading configuration data enables faster entry of configuration data because it allows the user to use the same metadata xml file for multiple instances of entity configuration. In addition to SAML metadata upload, WSO2 Identity Server also supports SAML metadata download for resident Identity providers using Management Console and URL.
To configure through file upload:
-
Perform the preliminary configs.
-
Enter the required values as given below.
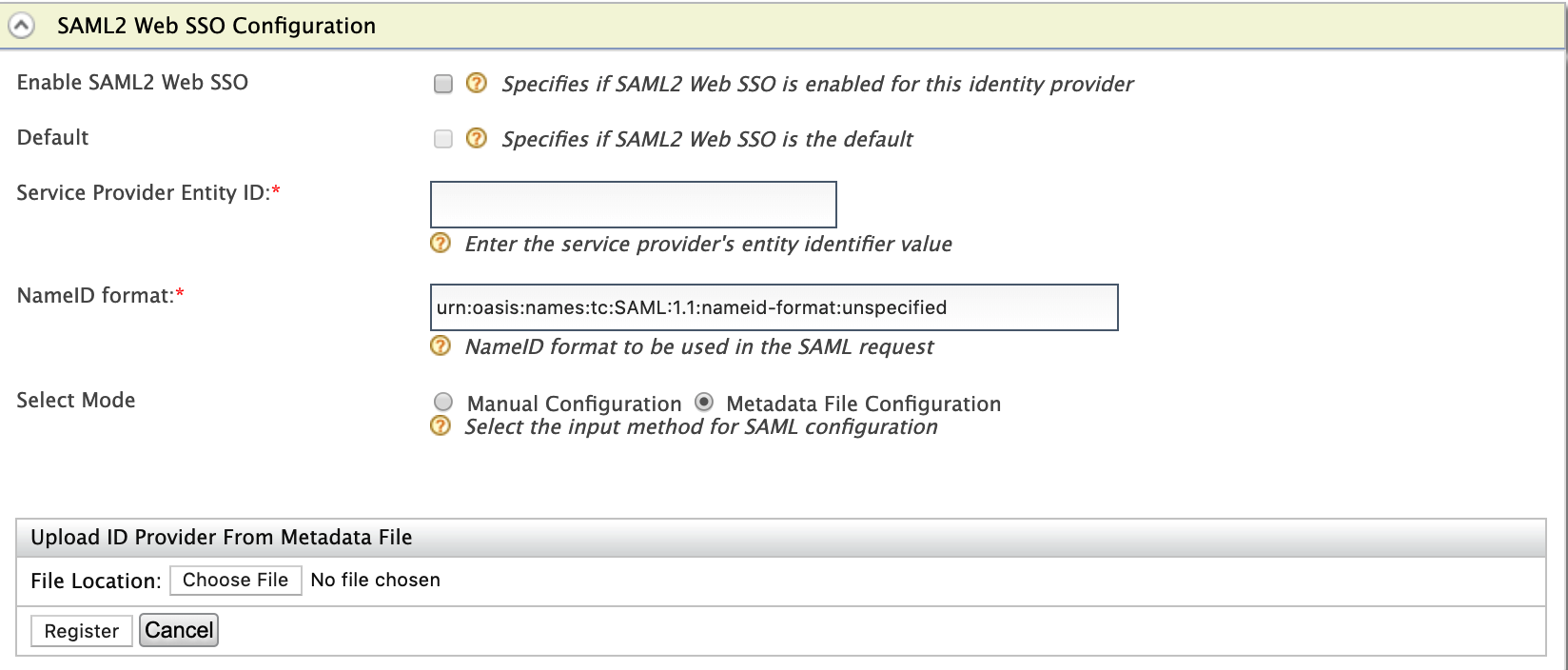
Field Description Sample Value
Select Mode Select the mode to decide the input method for SAML configuration. You can have manual configuration or Metadata data configuration where an .xmlmetadata file is uploaded.Metadata File ConfigurationFile Location This is to upload the IdP metadata file. Sample
<EntityDescriptor xmlns="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:metadata" entityID="example.com"> <IDPSSODescriptor WantAuthnRequestsSigned="false" protocolSupportEnumeration="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol"> <KeyDescriptor use="signing"> <KeyInfo xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"> <X509Data> <X509Certificate> -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIC+jCCAmOgAwIBAgIJAParOnPwEkKjMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBBQUAMIGKMQswCQYD VQQGEwJMSzEQMA4GA1UECBMHV2VzdGVybjEQMA4GA1UEBxMHQ29sb21ibzEWMBQG A1UEChMNU29mdHdhcmUgVmlldzERMA8GA1UECxMIVHJhaW5pbmcxLDAqBgNVBAMT I1NvZnR3YXJlIFZpZXcgQ2VydGlmaWNhdGUgQXV0aG9yaXR5MB4XDTEwMDcxMDA2 MzMwM1oXDTI0MDMxODA2MzMwM1owdjELMAkGA1UEBhMCTEsxEDAOBgNVBAgTB1dl c3Rlcm4xEDAOBgNVBAcTB0NvbG9tYm8xFjAUBgNVBAoTDVNvZnR3YXJlIFZpZXcx ETAPBgNVBAsTCFRyYWluaW5nMRgwFgYDVQQDEw9NeSBUZXN0IFNlcnZpY2UwgZ8w DQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADgY0AMIGJAoGBAN6bi0llFz+R+93nLLK5BmnuF48tbODp MBH7yGZ1/ESVUZoYm0GaPzg/ai3rX3r8BEr4TUrhhpKUKBpFxZvb2q+yREIeDEkD bHJuyVdS6hvtfa89WMJtwc7gwYYkY8AoVJ94gU54GP2B6XyNpgDTXPd0d3aH/Zt6 69xGAVoe/0iPAgMBAAGjezB5MAkGA1UdEwQCMAAwHQYDVR0OBBYEFNAwSamhuJSw XG0SJnWdIVF1PkW9MB8GA1UdIwQYMBaAFNa3YmhDO7BOwbUqmYU1k/U6p/UUMCwG CWCGSAGG+EIBDQQfFh1PcGVuU1NMIEdlbmVyYXRlZCBDZXJ0aWZpY2F0ZTANBgkq hkiG9w0BAQUFAAOBgQBwwC5H+U0a+ps4tDCicHQfC2SXRTgF7PlAu2rLfmJ7jyoD X+lFEoWDUoE5qkTpMjsR1q/+2j9eTyi9xGj5sby4yFvmXf8jS5L6zMkkezSb6QAv tSHcLfefKeidq6NDBJ8DhWHi/zvC9YbT0KkCToEgvCTBpRZgdSFxTJcUksqoFA== -----END CERTIFICATE----- </X509Certificate> </X509Data> </KeyInfo> </KeyDescriptor> <KeyDescriptor use="encryption"> <KeyInfo xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"> <X509Data> EwpDYWxpZm9ybmlhMRQwEgYDVQQHEwtTYW50YSBDbGFyYTEeMBwGA1UEChMVU3VuIE1pY3Jvc3lz dGVtcyBJbmMuMRowGAYDVQQLExFJZGVudGl0eSBTZXJ2aWNlczEcMBoGA1UEAxMTQ2VydGlmaWNh dGUgTWFuYWdlcjAeFw0wNzAzMDcyMjAxMTVaFw0xMDEyMDEyMjAxMTVaMDsxFDASBgNVBAoTC2V4 YW1wbGUuY29tMSMwIQYDVQQDExpMb2FkQmFsYW5jZXItMy5leGFtcGxlLmNvbTCBnzANBgkqhkiG HREEETAPgQ1tYWxsYUBzdW4uY29tMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBBAUAA0EAEgbmnOz2Rvpj9bludb9lEeVa OA46zRiyt4BPlbgIaFyG6P7GWSddMi/14EimQjjDbr4ZfvlEdPJmimHExZY3KQ== </X509Data> </KeyInfo> </KeyDescriptor> <ArtifactResolutionService isDefault="true" index="0" Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:SOAP" Location="https://example.com/SAML/Artifact"/> <SingleLogoutService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:SOAP" Location="https://example.com/SAML/SLO/SOAP"/> <SingleLogoutService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect" Location="https://example.com/SAML/SLO/Browser" ResponseLocation="https://example.com/SAML/SLO/Response"/> <SingleLogoutService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect"/> <SingleLogoutService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:SOAP"/> <ManageNameIDService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect" ResponseLocation="https://example.com:9443/amserver/IDPMniRedirect/metaAlias/idp"/> <ManageNameIDService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:SOAP" Location="https://example.com:9443/amserver/IDPMniSoap/metaAlias/idp"/> <NameIDFormat> urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent </NameIDFormat> <NameIDFormat> urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient </NameIDFormat> <SingleSignOnService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect" Location="https://example.com:9443/amserver/SSORedirect/metaAlias/idp"/> <SingleSignOnService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:SOAP" Location="https://example.example.com:9443/amserver/SSOSoap/metaAlias/idp"/> </IDPSSODescriptor> </EntityDescriptor> -
Click Register.
Advanced Configs¶
Configure ACL URL in a production environment
The default assertion consumer URL that is sent with the SAML request includes the local domain and default port. In a production environment, you may need to change the assertion consumer URL. To do this, follow the steps given below:
- Open the
<IS_HOME>/repository/conf/deployment.tomlfile and add the following configuration. -
Update the assertion consumer URL as required.
[authentication.authenticator.saml] enable=true SAMLSSOAssertionConsumerUrl="https://localhost:9443/commonauth"
Configuring hostname verification
-
In previous releases, SAML Single-Logout (SLO) requests for service providers were initiated without hostname verification which can impose a security risk. From IS 5.2.0 release onwards, certificate validation has been enforced and hostname verification is enabled by default. If you want to disable the hostname verification, open the
<IS_HOME>/repository/conf/deployment.tomlfile and add the following configuration.[saml.slo] host_name_verification: false -
If the certificate is self-signed, import the service provider's public key to the IS client trust store to ensure that the SSL handshake in the SLO request is successful. For more information on how to do this, see Managing Keystores with the UI in the WSO2 Product Administration Guide.
Related Topics
- Identity Federation is part of the process of configuring an identity provider. For more information on how to configure an identity provider, see Configuring an Identity Provider.
- See Configuring Shibboleth IdP as a Trusted Identity Provider for a sample of using SAML2 Web SSO configuration.