JSON Web Key Set¶
What is JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)?¶
The JSON Web Key Set (JWKS) endpoint is a read-only endpoint that returns the authorization server's public key set in the JWKS format. This contains the signing key(s) that the Relying Party (RP) uses to validate signatures from the server. For more information on this endpoint, see the OpenID Connect Discovery specification.
Usage of JWKS¶
The main benefit of allowing JWKS endpoint configuration is its ability to handle key rotation by external identity providers. Configuring this endpoint would enable you to programmatically discover JSON web keys and allow the third party identity providers to publish new keys without having the overhead of notifying each and every client application. This allows smooth key rollover and integration.
How does it work?¶
The following sequence diagram illustrates the scenario where a JWT obtained from a third party IdP is validated using the JWKS-based JWT Validator.
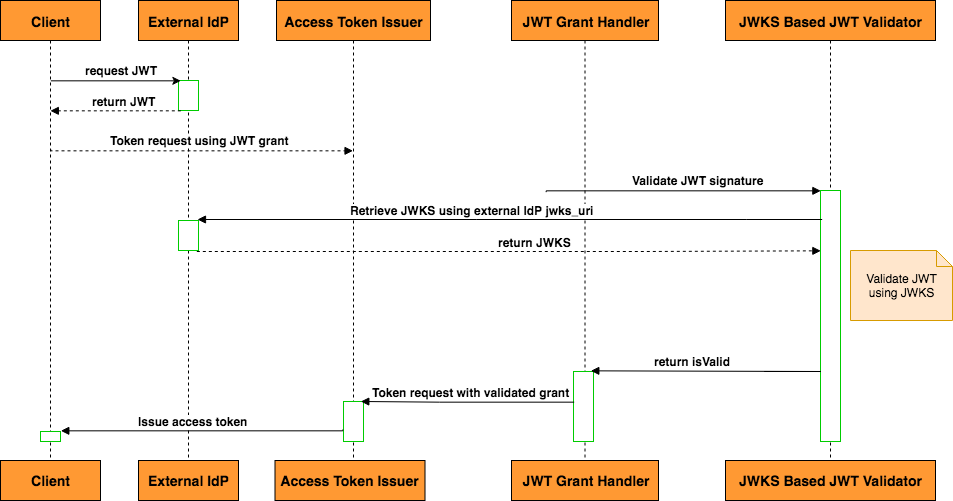
The steps of the above diagram are explained below:
Step 1:
-
User requests a JWT assertion from the identity provider.
-
A valid JWT is returned with the response.
Step 2:
-
The user initiates a token request to WSO2 Identity Server’s token endpoint using JWT grant type with the obtained JWT assertion.
-
Access token issuer handles all the requests sent to the token endpoint.
Step 3:
-
Access token issuer invokes the JWT grant handler to validate the provided JWT assertion.
-
Deploys and configures the JWT client-handler artifacts.
Step 4:
- JWT grant handler invokes the JWKS based JWT validator to validate the JWT signature using IdP’s jwks endpoint.
Step 5:
- JWKS based JWT validator validates the JWT using IdP’s JWKS.
Step 6:
- Upon JWT grant validation, access token issuer issues a new access token to the user.
Here, the retrieved JWKS is cached against the jwks_uri. When validating a JWT, we use the 'kid' header parameter which is an indicator for the key used to sign the JWT at the IdP, and compare it against the JWKS 'kid' properties. If a matched 'kid' is found among the key set, the JWT will be validated using the corresponding key. In case of key rollover at the IdP, the JWT is signed using the new keys and hence the matching key is not found in the cached JWKS. When a matching key is not found, the validator retrieves the latest JWKS from the IdP JWKS endpoint and obtain the matching key for signature validation.
Sample JSON Web Key Set¶
The default JWKS of WSO2 Identity Server is as follows.
{
"keys":[
{
"kty":"RSA",
"e":"AQAB",
"use":"sig",
"kid":"ZjRmYTMwNTJjOWU5MmIzMjgzNDI3Y2IyMmIyY2EzMjdhZjViMjc0Zg",
"alg":"RS256",
"n":"j3mYMT8N2SR8cpimdMOTpk_M8fOxPF1BHQAiCtld4nbksILgJKsA34GSP5Oh4gLW21VCEPPzdGLnqfwM6ZoG_X0rcK5--VbqH_vH4Cclba6fqlLxCvTiRbPJ58Pe7-biCeQ368dG2aeBPV3EhO8br3Z_LcQXASmhSWps8J3GOSx_49xzkHh59J2gJHhnvjxcszZAF35SLAb6F-2rJQrOJs6u7WfJv4NQxSyhcgcr4_-77JzNFEVUj4TPSBy2WGAgK5ttP5-kG3-rKs0lQjTo9h_hK89KjbbRvoqZdpxnwQYxFDOk0CxijZVO5Cs3cabeUHZeXehHSgXj6W-VGMiDgw"
},
{
"kty":"RSA",
"e":"AQAB",
"use":"sig",
"kid":"ZjRmYTMwNTJjOWU5MmIzMjgzNDI3Y2IyMmIyY2EzMjdhZjViMjc0Zg_RS256",
"alg":"RS256",
"n":"j3mYMT8N2SR8cpimdMOTpk_M8fOxPF1BHQAiCtld4nbksILgJKsA34GSP5Oh4gLW21VCEPPzdGLnqfwM6ZoG_X0rcK5--VbqH_vH4Cclba6fqlLxCvTiRbPJ58Pe7-biCeQ368dG2aeBPV3EhO8br3Z_LcQXASmhSWps8J3GOSx_49xzkHh59J2gJHhnvjxcszZAF35SLAb6F-2rJQrOJs6u7WfJv4NQxSyhcgcr4_-77JzNFEVUj4TPSBy2WGAgK5ttP5-kG3-rKs0lQjTo9h_hK89KjbbRvoqZdpxnwQYxFDOk0CxijZVO5Cs3cabeUHZeXehHSgXj6W-VGMiDgw"
}
]
}| Property Value | Description |
|---|---|
| kty | The public key type. |
| e | The exponent value of the public key. |
| use | Implies how the key is being used. The value sig represents signature. |
| kid | The thumbprint of the certificate. This value is used to identify the key that needs to be used to verify the signature. |
| alg | The algorithm used to secure the JSON Web Signature. |
| n | The modulus value of the public key. |