User Managed Access (UMA 2.0)¶
What is UMA 2.0?¶
UMA 2.0 (User Managed Access) is a federated authorization standard protocol approved by the Kantara Initiative. It is built on top of OAuth 2.0 and enables party-to-party sharing.
UMA enables users to share and control access to their protected resources with other parties that request access to them. Additionally, it also strengthens data privacy and helps to comply with modern-day privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. For instance, consider a patient who wishes to share their health data (such as medical prescriptions and lab reports) with their doctor, family members, and health insurance company. They may wish to selectively share some health-related data with certain parties, but may not want to share everything with everyone, and may wish to give them permission to view the data, but not edit it. UMA 2.0 helps to effectively share this data as well as maintain control over the resource sharing in a secure and reliable manner.
This is done using authorization policies. The specialty of this protocol is that resource owners need not be present online at the time of access, because the cross-party sharing is driven by predefined policies.
How does it work?¶
UMA works by defining a workflow that creates authorization policies on a centralized authorization server. There are five main roles associated with a UMA workflow.
-
Resource owner: The user or entity that grants access to a protected resource
-
Resource server: Hosts the protected resources. The resource server is capable of accepting and responding to requests to access protected resources.
-
Authorization server: Protects the resources in the resource server on behalf of the resource owner. WSO2 Identity Server usually acts as the authorization server.
-
Client: An application that acts on behalf of the requesting party
-
Requesting party: An entity that seeks to access a protected resource using a client
The flow¶
-
The resource owner registers the resource at the resource server and sets policy conditions at the authorization server.
-
The requesting party requests access to the protected resource using the client.
-
The client, acting on behalf of the requesting party, interacts with the authorization server and provides the required claims that satisfy the resource owner's authorization policies.
-
The client then receives a token from the authorization server.
-
The token is presented to the resource server in order to obtain access for the requesting party.
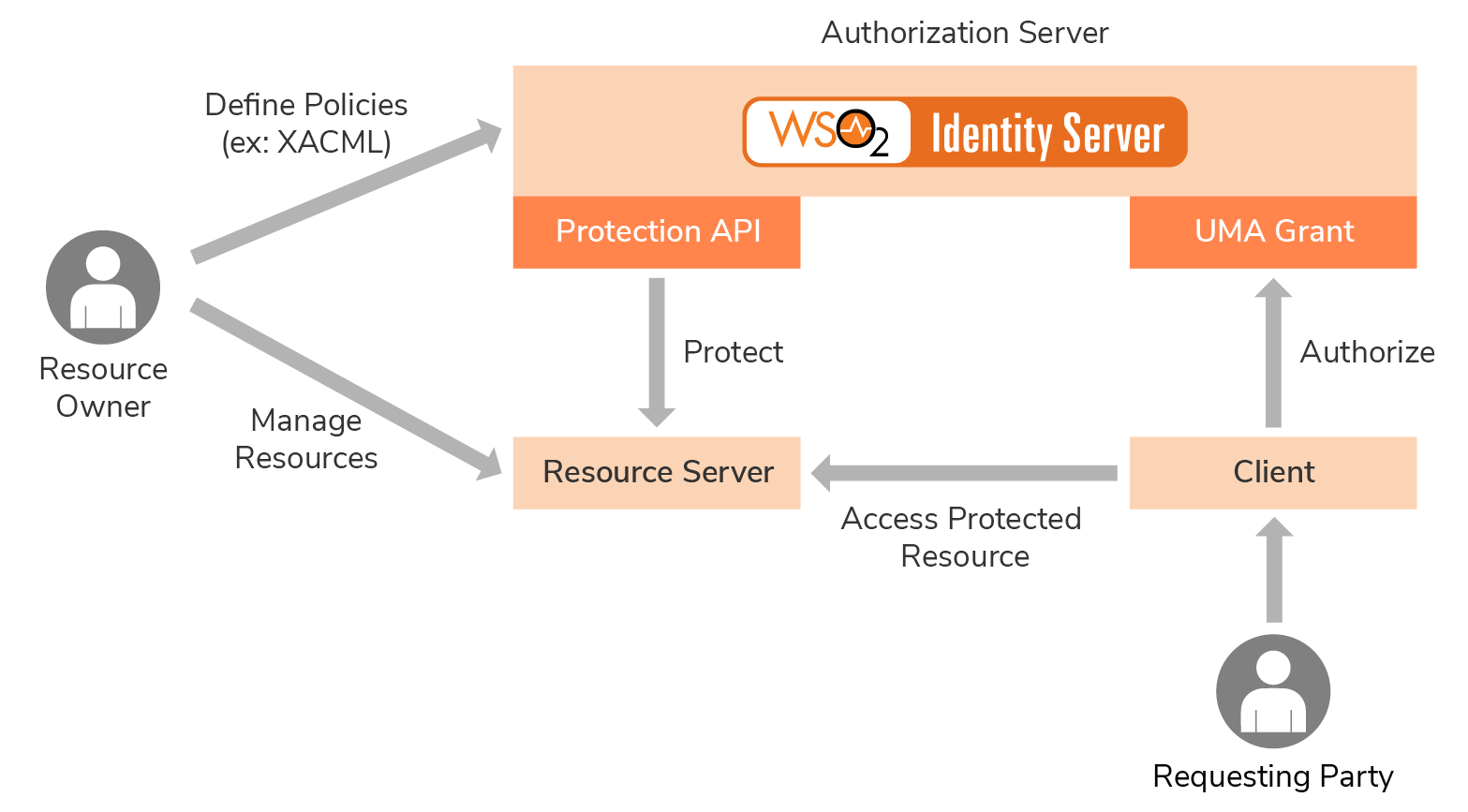
Architecture of the UMA profile¶
The UMA profile consists of two main components as shown in the diagram given above.
- Protection API
- UMA grant
Protection API¶
The protection API provides the following endpoints:
-
Resource Registration Endpoint: provides a means for the resource server to register resources under the protection of the authorization server on behalf of the resource owner, and manages these resources over time.
-
Permission Endpoint: provides a means for the resource server to request permission(s) when the client’s resource request is unaccompanied by an RPT (Requesting Party Token) or is accompanied by an invalid RPT.
Info
An RPT is an OAuth access token that is unique to a requesting party, client, authorization server, resource server, and resource owner. It is associated with the UMA grant. This token also contains information about granted permissions.
-
Token Introspection Endpoint (optional): provides a means for the resource server to introspect the RPT, which is required to access a UMA protected resource.
Tip
For more detailed information about each of these endpoints, and sample requests and responses, see Resource Registration Endpoint or Permission Endpoint.
When the resource server makes an access request to the authorization server, it needs to access these three endpoints of the Protection API. In order to access the protection API, it is a must for the request made by the resource server to be accompanied by an access token, namely a Protection API Access Token (PAT).
PAT is simply an OAuth access token with the scope uma_protection, which represents the resource owner’s authorization to use the protection API. It uniquely represents the resource owner, the resource server used for resource management, and the authorization server used for the protection of these resources.
Info
For more information, refer Federated Authorization for User-Managed Access (UMA) 2.0.
UMA grant¶
The UMA grant is an extension of the OAuth 2.0 grant and enhances OAuth capabilities by enabling the following:
-
party-to-party authorization: the resource owner can authorize access to their protected resource for clients used by entities that are in a requesting party role.
-
predefined authorization grant rules: the resource owner can configure authorization grant rules (policy conditions) at will rather than having to authorize access token issuance each time synchronously. The authorization server and resource server, interact with the client and requesting party asynchronously, with respect to the resource owner's interactions.
Info
For more information, refer User-Managed Access (UMA) 2.0 Grant for OAuth 2.0 Authorization.
Using the UMA grant, a client application acting on behalf of the requesting party can obtain a Requesting Party Token (RPT) from the authorization server after successful evaluation of policy conditions, scopes, claims, and any other relevant information.
Related topics