Configure Google as a Federated Authenticator¶
This page guides you through configuring Google as a federated authenticator in WSO2 Identity Server.
Set up a Google app¶
-
Go to the Google Developer console, create a new project or select an existing project.
-
If the APIs & services page isn't already open, do the following:
-
Open the navigation menu and click View all products.
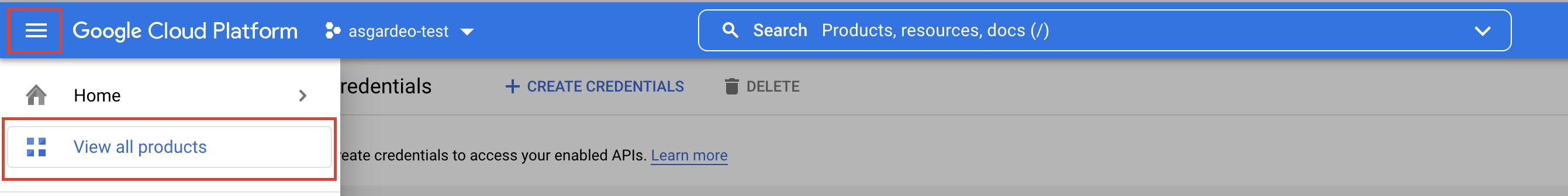
-
Under Management, click APIs & Services.
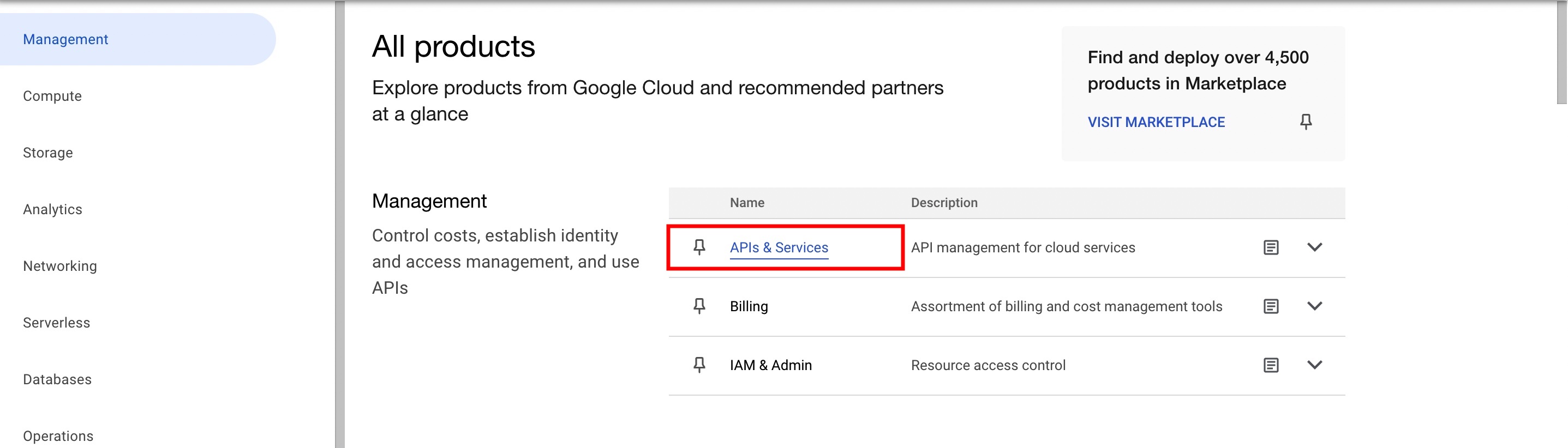
-
-
Go to the Credentials page, click Create Credentials, and select Oauth client ID.
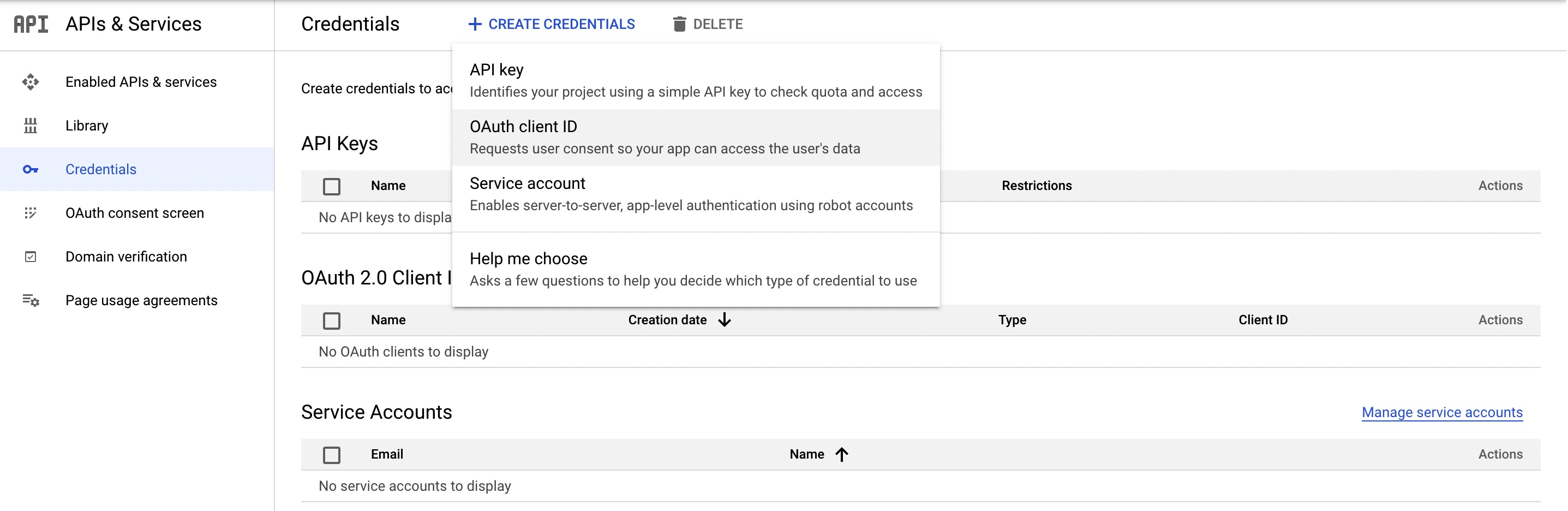
-
Configure your consent screen by clicking Configure Consent Screen and return to Create OAuth client ID screen once you are done.
Info
For more information, see User Consent
-
Select the Web application as the application type.
-
Provide a name for your app and the following URL as the Authorized Redirect URI of the application:
7. Take note of the client ID and client secret generated for the application.https://<IS_HOST>:<IS_PORT>/commonauth
Register an identity provider¶
-
Log in to the Management Console(
https://<IS_HOST>:<PORT>/carbon) using admin/admin credentials. -
Navigate to Main > Identity > Identity Providers > Add.
-
Enter an Identity Provider Name, Display Name, and Description.
-
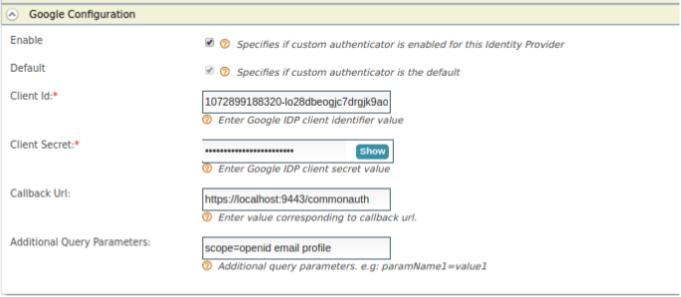
Go to Google Configuration under Federated Authenticators.
-
Select the checkbox Enable.
-
Configure the Client ID and Client Secret that were received after creating the Google application client.
-
Configure the Callback URL as
https://<IS_HOST>:<IS_PORT>/commonauth -
Click on Register to add the Google IdP.
Register a service provider¶
To register your application as a service provider in the WSO2 Identity Server:
-
Log in to the WSO2 Identity Server Management Console using administrator credentials.
-
Go to Main > Identity > Service Providers > Add.
-
Enter a Service Provider Name. Optionally, enter a Description.
-
Click Register.
-
In the Inbound Authentication Configuration section, click Configure under the OAuth/OpenIDConnect Configuration section and set the configurations as required.
-
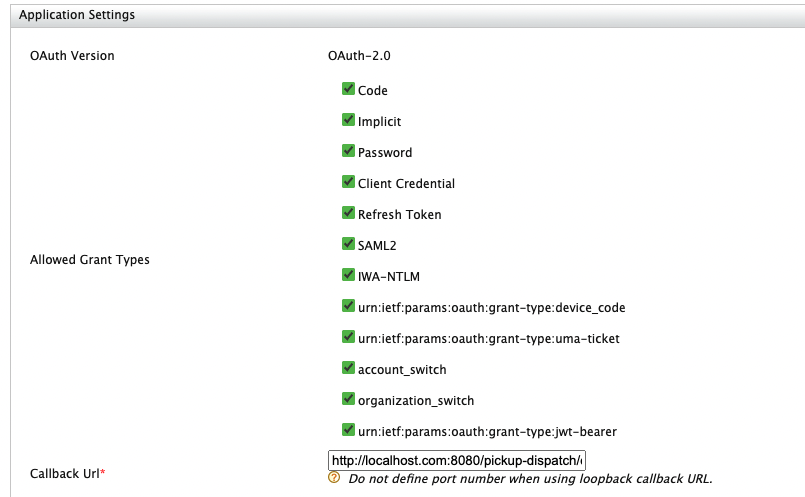
Configure the Callback URL of the sample application (http://localhost.com:8080/pickup-dispatch/oauth2client).
-
Keep the other configurations as default and click on Add
-
Click Register. Now you will be sent back to the Service Providers page.
-
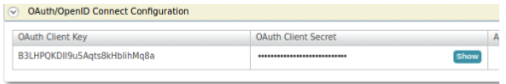
Take a copy of the OAuth Client Key and the OAuth Client Secret for later usages
-
Go to the Local and Outbound Authentication Configuration section.
-
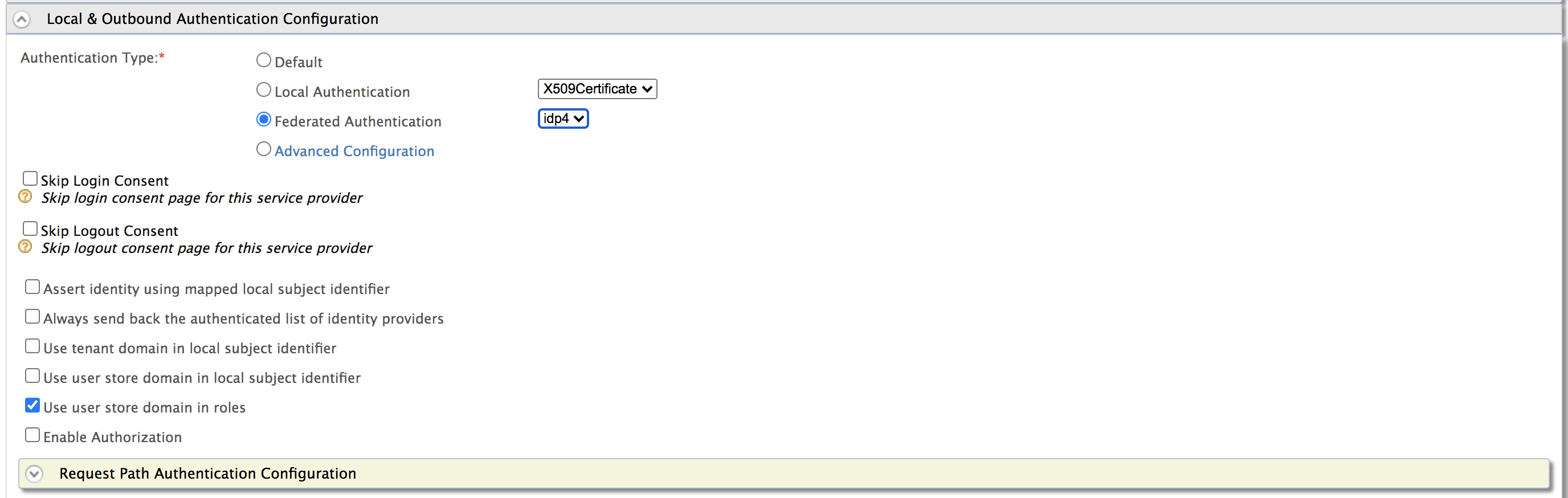
For Authentication Type, select the Federated Authentication radio button and select the Identity Provider you created from the dropdown list under Federated Authentication.
-
Click Update to save the changes.
Try it out¶
You have successfully configured Google as your federated authenticator. Now, when you try to login to your application, it should redirect to the Google login page. On successful authentication with your Google credentials, you will be able to access your application.
Set up the sample app¶
-
Download Apache Tomcat 9.x from here and install. Tomcat server installation location will be referred as
<TOMCAT_HOME>later in this guide. -
It is recommended that you use a hostname that is not
localhostto avoid browser errors. Modify the/etc/hostsentry in your machine to reflect this. Note thatwso2is.localis used in this documentation as an example, but you must modify this when configuring the authenticators or connectors with this sample application. -
Download the sample from GitHub.
- Navigate to WSO2 Identity Server Samples.
- Download the
pickup-dispatch.warfile from the latest release assets.
Deploy the sample app¶
Deploy this sample web app on a web container.
-
Copy the
pickup-dispatch.warfile into thewebappsfolder. For example,<TOMCAT_HOME>/apache-tomcat-<version>/webapps -
Open a terminal window and add the following entry to the
/etc/hostsfile of your machine to configure the hostname.127.0.0.1 wso2is.local 127.0.0.1 localhost.comWhy is this step needed?
Some browsers do not allow you to create cookies for a naked hostname, such as
localhost. Cookies are required when working with SSO . Therefore, to ensure that the SSO capabilities work as expected in this tutorial, you need to configure theetc/hostfile as explained in this step.The
etc/hostfile is a read-only file. Therefore, you won't be able to edit it by opening the file via a text editor. Instead, edit the file using the terminal commands.
For example, use the following command if you are working on a Mac/Linux environment.sudo nano /etc/hosts -
Open the
dispatch.propertiesfile found in the<TOMCAT_HOME>/webapps/pickup-dispatch/WEB-INF/classesdirectory and edit the consumerKey and consumerSecret with the values obtained from the OAuth configuration. -
Restart the Tomcat server.
Log in¶
-
To test the sample, go to the following URL:
http://<TOMCAT_HOST>:<TOMCAT_PORT>/pickup-dispatch.
For example.http://localhost.com:8080/pickup-dispatch
-
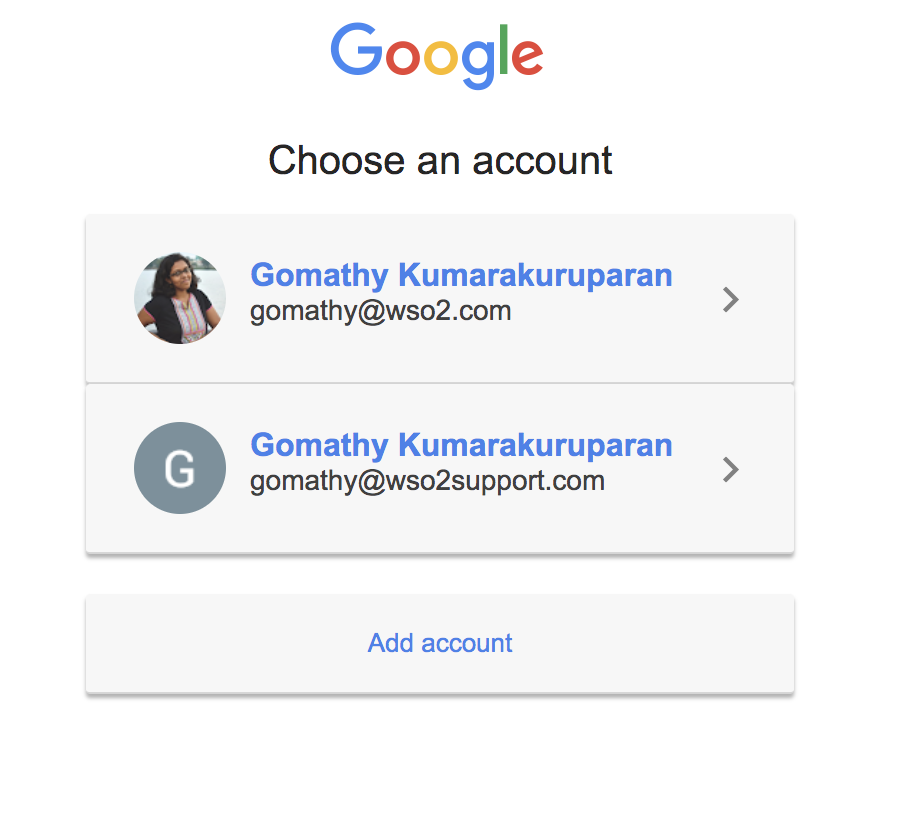
Click Login. You are redirected to the Google login page.
-
Sign in using your Google credentials. You are redirected to the Pickup sample homepage.
Related topics