Seperate Databases for Clustering¶
WSO2 Identity Server uses a database to store information such as user management details and identity data. By default, WSO2 Identity Server is shipped with an embedded H2 database that works for all types of data.
This section guides you through the logical separation of data that you can do when clustering WSO2 Identity Server.
Embedded H2 is NOT RECOMMENDED in production
The embedded H2 database is not recommended for enterprise testing and production environments. It has lower performance, and clustering limitations, and can cause file corruption failures. Therefore, use an industry-standard RDBMS such as Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, or MS SQL instead.
Before you begin
Creating separate databases as shown below is not mandatory. Instead, you can point to all the following data sources according to the default data structure. This will not make a difference in performance.
The following image shows the default database structure and a recommended database structure for the logical separation of data.
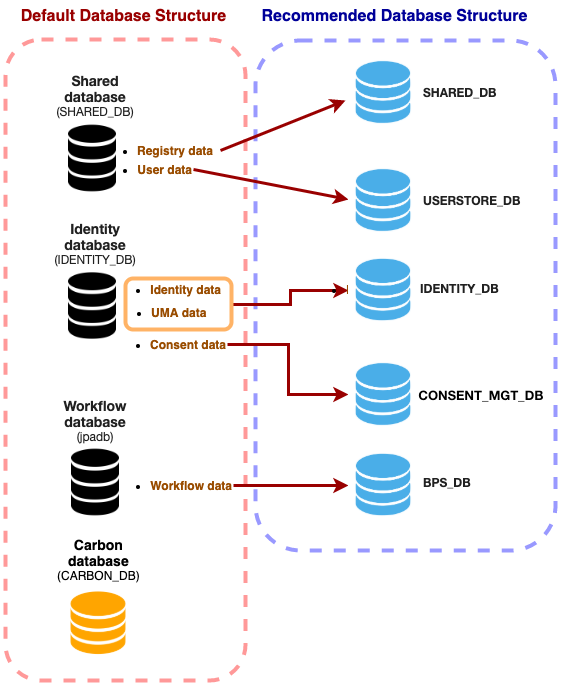
| Database Name | Description |
|---|---|
USERSTORE_DB |
SHARED_DB.
. |
IDENTITY_DB |
IDENTITY_DB. In a deployment, both identity and UMA can be configured in a single database while consent data is configured to a separate database `CONSENT_MGT` |
BPS_DB |
|
SHARED_DB |
SHARED_DB.
During a deployment, user data can be configured to a different database, USERSTORE_DB while the registry
data remains in the SHARED_DB
. |
CONSENT_MGT |
IDENTITY_DB.
In a deployment, both identity and UMA can be configured in a single database while consent data is configured to a separate database. |