OAuth2 Pushed authorization requests (PAR)¶
Generally, when a user logs in to a web application using a user agent, such as a web browser, an OAuth 2.0 authorization request is initiated from the front-channel. This introduces two major challenges,
-
The authorization payload is sent through query strings in a URL. Therefore, the authorization server cannot guarantee the integrity of the authorization payload.
-
Complex authorization requests can sometimes be too large for browsers to process.
The PAR specification defines the /par endpoint in an authorization server to mitigate these issues.
During a PAR initiated login, first, the back-channel sends the authorization payload directly to the /par endpoint of the authorization server. The /par endpoint, in response, returns a reference to the authorization payload called the request_uri.
After this interaction, the usual OAuth flow takes place in the front-channel. But, instead of including the complete authorization payload in the URL, the new authorization request contains only the client ID of the application and the request_uri.
Therefore, using PAR with an OAuth authorization request,
- ensures integrity of the request is protected.
- ensures confidentiality of the request.
- enables complex requests to be passed without browser limitations.
- avoids leakage of query strings to third-party sites and web server logs.
How does it work?¶
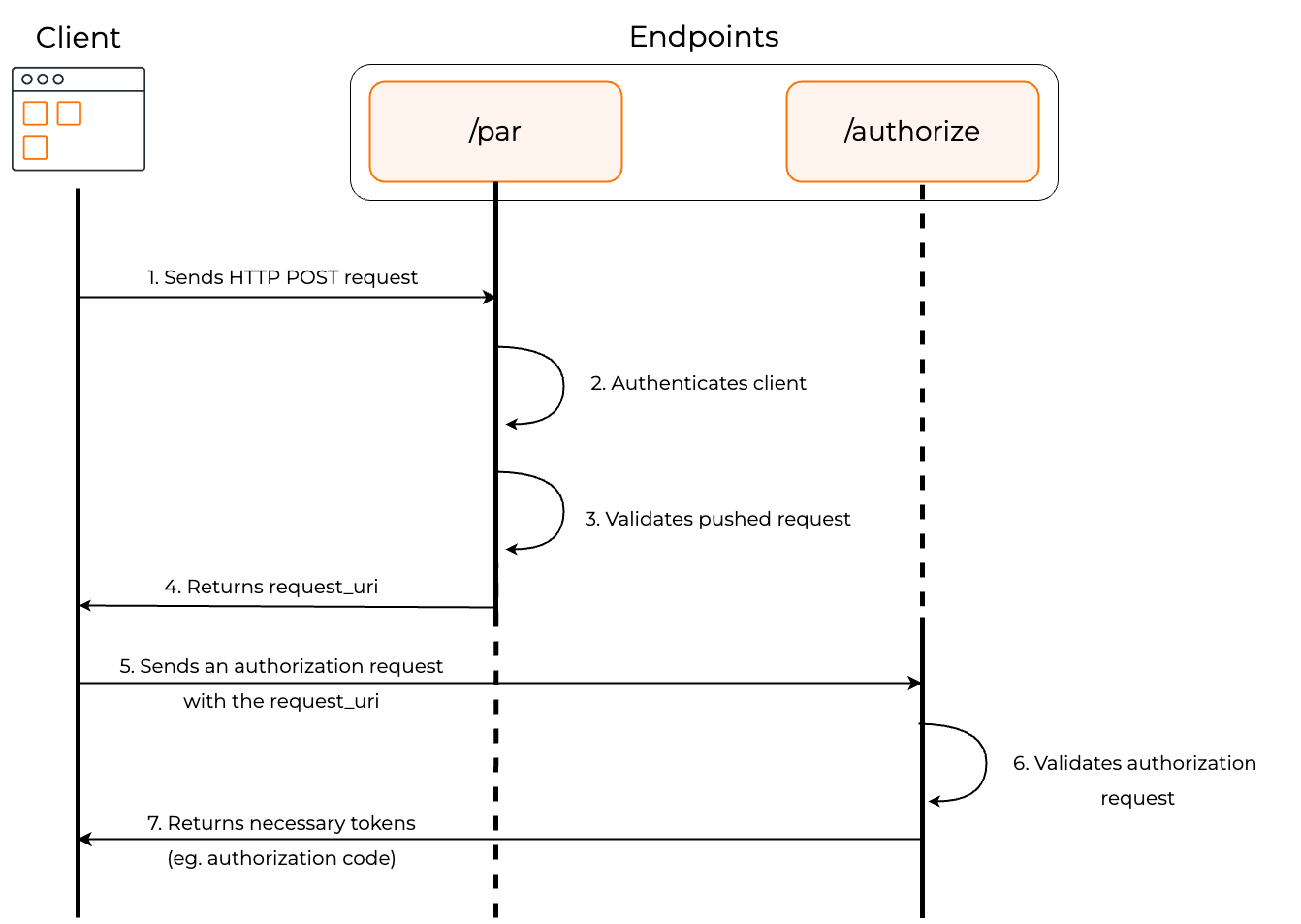
The diagram below illustrates the PAR authorization flow.
-
The client makes a POST request to the
/parendpoint along with all the parameters required for authorization. -
The authorization server authenticates the client.
-
The endpoint validates the pushed authorization request.
-
If the validation is successful, the endpoint returns a response containing the
request_uri, which functions as the reference to the authorization payload. -
The client makes an authorization request to the authorization endpoint with the client ID and the request_uri.
-
The
/authorizeendpoint validates the request. -
If the validation is successful, the client receives the authorization code (or the access token based on the chosen grant type).