OAuth2 grant types of WSO2 Identity Server applications¶
OAuth 2.0 defines several grant types used to obtain an access token, which is required to access protected resources on behalf of a user or an application. Each grant type is designed for a specific use case and supports different parameters.
The grant types supported by WSO2 Identity Server applications are as follows:
OAuth 2.0 grants
- Authorization code grant
- Refresh token grant
- Client credentials grant
- Implicit grant
- Password grant
- Token exchange grant
- SAML 2.0 bearer grant
WSO2 Identity Server's custom grants
Note
WSO2 Identity Server provides more control over issuing id tokens and user claims for client-credential grant type.
To facilitate this, add the following configurations to the deployment.toml file found in the
<IS_HOME>/repository/conf folder in order to register new ScopeHandlers and ScopeValidators.
[oauth.custom_scope_validator]
class = "org.fully.qualified.class.name.CustomScopeValidator"
Further, by configuring the <IdTokenAllowed> property to true or false along with the above configuration,
you can turn on or turn off the process of issuing ID tokens for the grant types that have the openid scope.
By default, IdTokenAllowed is set to true, you can allow it to issue id_tokens for all grant types that have
the openid scope. By configuring it to false, you can stop issuing ID tokens.
Note: You can not turn off the process of issuing ID tokens for the authorization_code grant type.
By configuring the <IsRefreshTokenAllowed> property to true or false along with the above configuration,
you can turn on or turn on the process of issuing refresh tokens. By default, IsRefreshTokenAllowed is set to
true, and you can allow it to issue refresh tokens for all grant types. By configuring it to false, you can stop
issuing refresh tokens.
Note: By default, issuing ID token for client_credentials grant type is disabled as it is logically invalid.
By configuring the <PublicClientAllowed> property to true or false along with the above configuration,
you can decide whether the grant type can be used by public clients or not. By default, PublicClientAllowedis set
to true, and you can allow it to be used by public clients. By configuring it to false, you can stop using the
grant type in public clients.
Note: By default, using client_credentials grant type for public clients is disabled as it is logically invalid.
Authorization code grant¶
The Authorization code flow provides a secure way for a client application to obtain an access token without exposing the user's credentials to the client application. The user only authenticates with the authorization server, which then issues an authorization code that can be exchanged for an access token.
This helps to protect the user's credentials and prevents them from being compromised by malicious client applications.
The following diagram shows how the authorization code flow works.
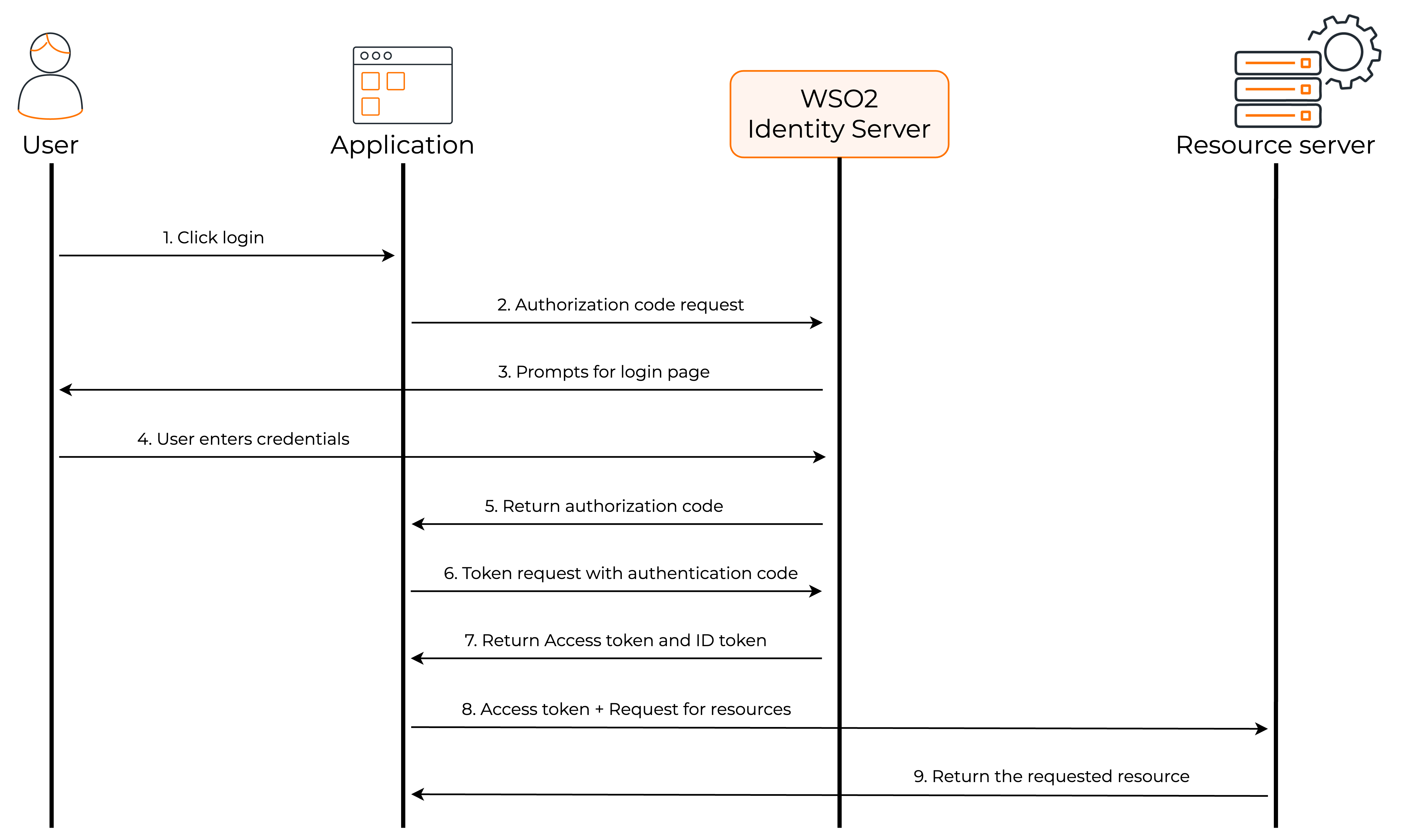
- The user visits the client application and requests for login through WSO2 Identity Server.
- The client application redirects the authorization code request to WSO2 Identity Server.
- WSO2 Identity Server prompts the user to enter credentials.
- The user enters the credentials.
- After successful authentication, WSO2 Identity Server sends the authorization code to the client application.
- The client application uses this authorization code to request an access token from WSO2 Identity Server.
- WSO2 Identity Server sends the access token and ID token to the client application.
- The client application can now request user information from the resource server by providing the access token.
- The resource server returns the requested user information to the client application.
Refresh token grant¶
The refresh token grant provides a secure way for client applications to obtain a new access token without requiring the user to re-authenticate. This can help improve the user experience by avoiding unnecessary login prompts and reducing the load on the authorization server by reducing the frequency of authentication requests. Refresh tokens typically have a longer lifetime than access tokens, and the user or the authorization server can revoke them at any time.
The following diagram shows how the refresh token flow works.
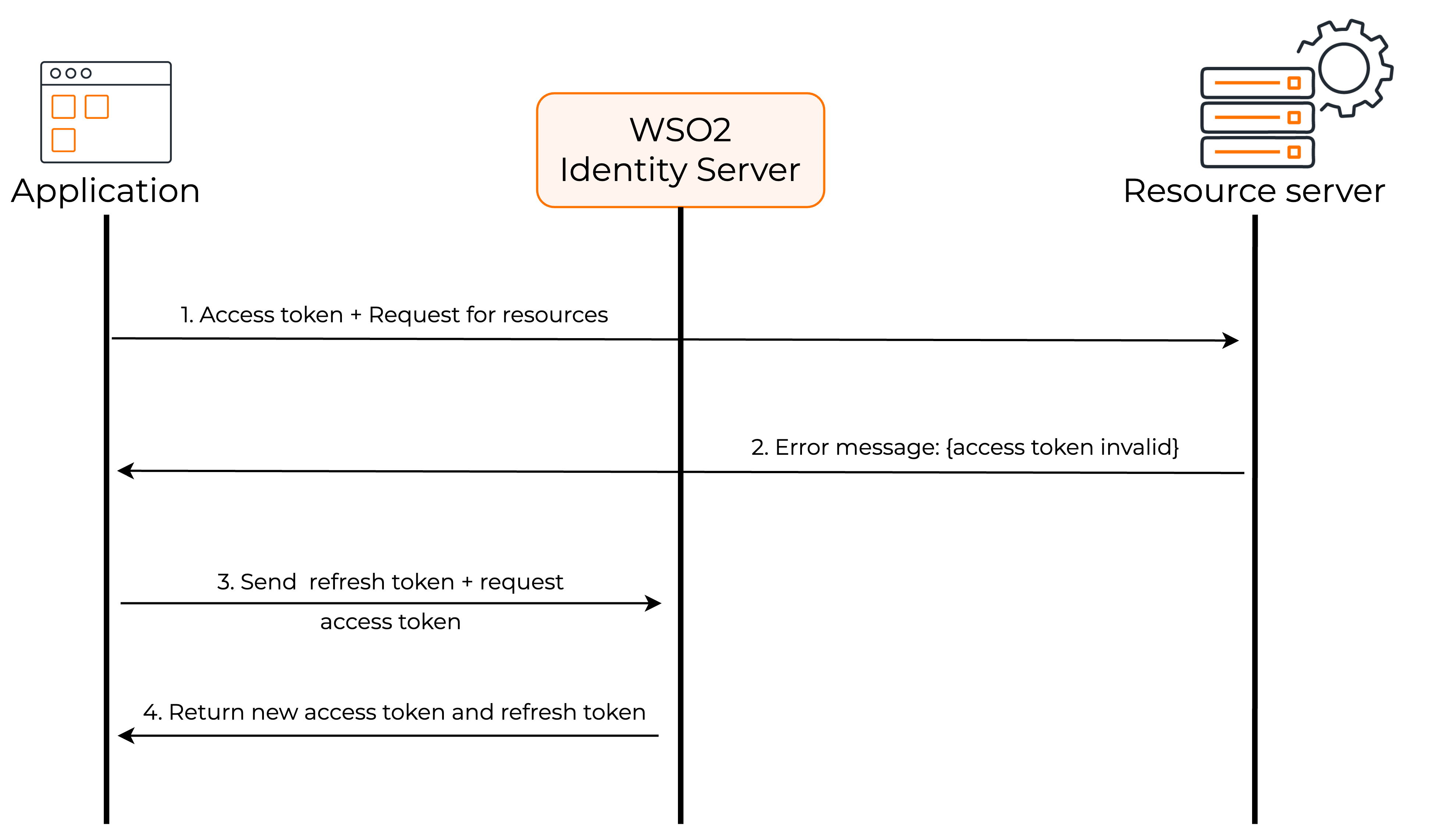
- The client application requests user information from the resource server by providing the access token.
- As the access token is expired, the resource server returns an error message.
- By sending the refresh token, the client application requests a new access token from WSO2 Identity Server.
- WSO2 Identity Server sends a new access token and a new refresh token.
Client credentials grant¶
The client credentials flow provides a secure way for client applications to obtain an access token without user authentication. This can be useful in scenarios where the client application needs to access its own resources, such as data storage or APIs, but does not require access to user data. However, it is important to ensure that the client credentials are kept secure, as any party that posses these credentials can obtain access tokens and access the client's resources.
The following diagram shows how the client credentials grant flow works.
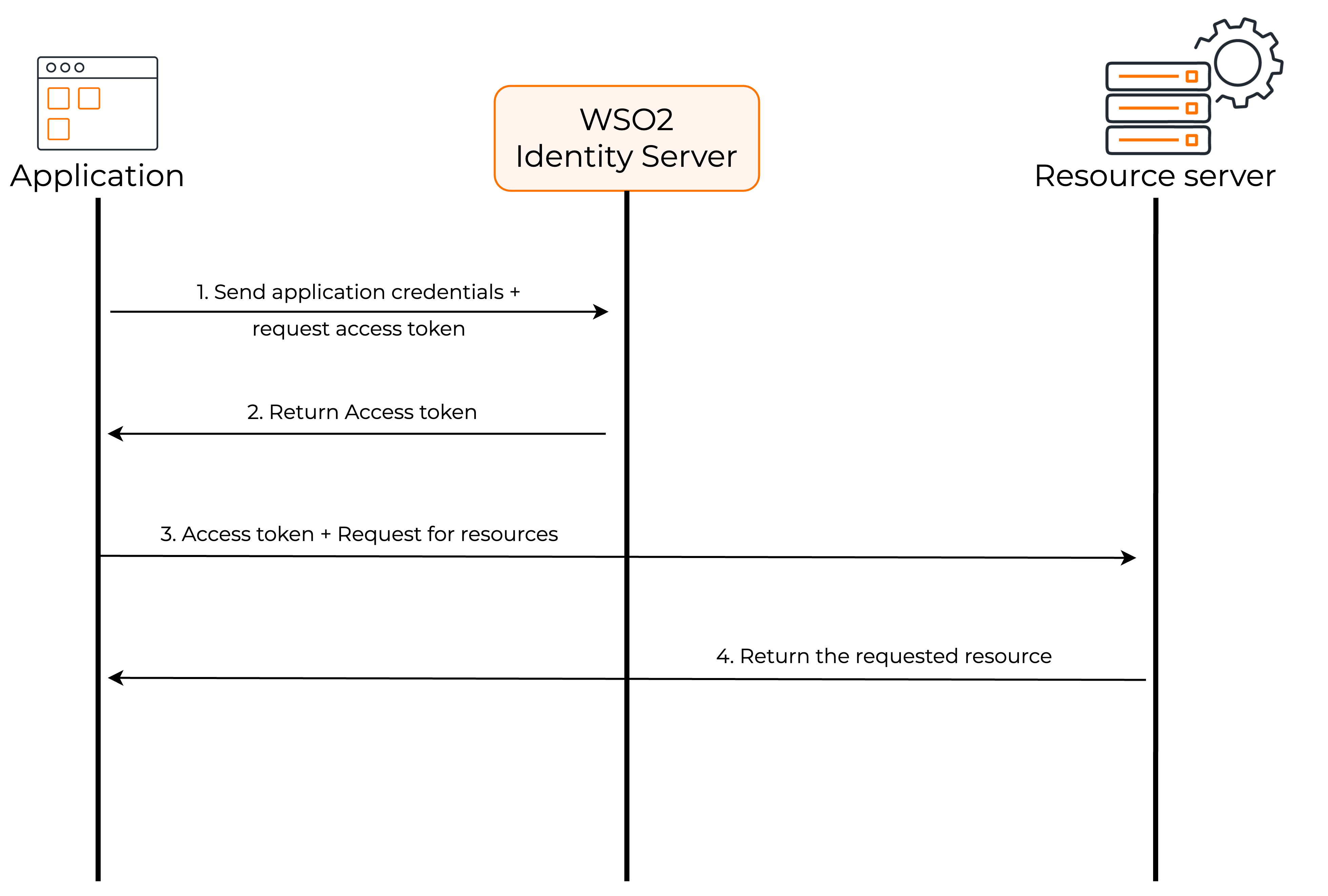
- The client application sends its credentials (
client_idandclient_secret) to WSO2 Identity Server and requests an access token. - WSO2 Identity Server sends the access token to the client application.
- The client application can now request user information from the resource server by providing the access token.
- The resource server returns the requested user information to the client application.
Implicit grant¶
Note
WSO2 Identity Server does not recommend using implicit grant in it's applications.
The implicit grant flow is an OAuth 2.0 grant type that enables a client application to obtain an access token directly from the authorization server without an intermediate authorization code exchange. This flow is commonly used in browser-based applications where the client application runs in a web browser.
However, it is important to note that the access token is exposed in the browser's URL fragment, which can make it vulnerable to certain types of attacks, such as cross-site scripting (XSS). As a result, this flow is typically not recommended for applications that require high security.
The following diagram shows how the implicit grant flow works.
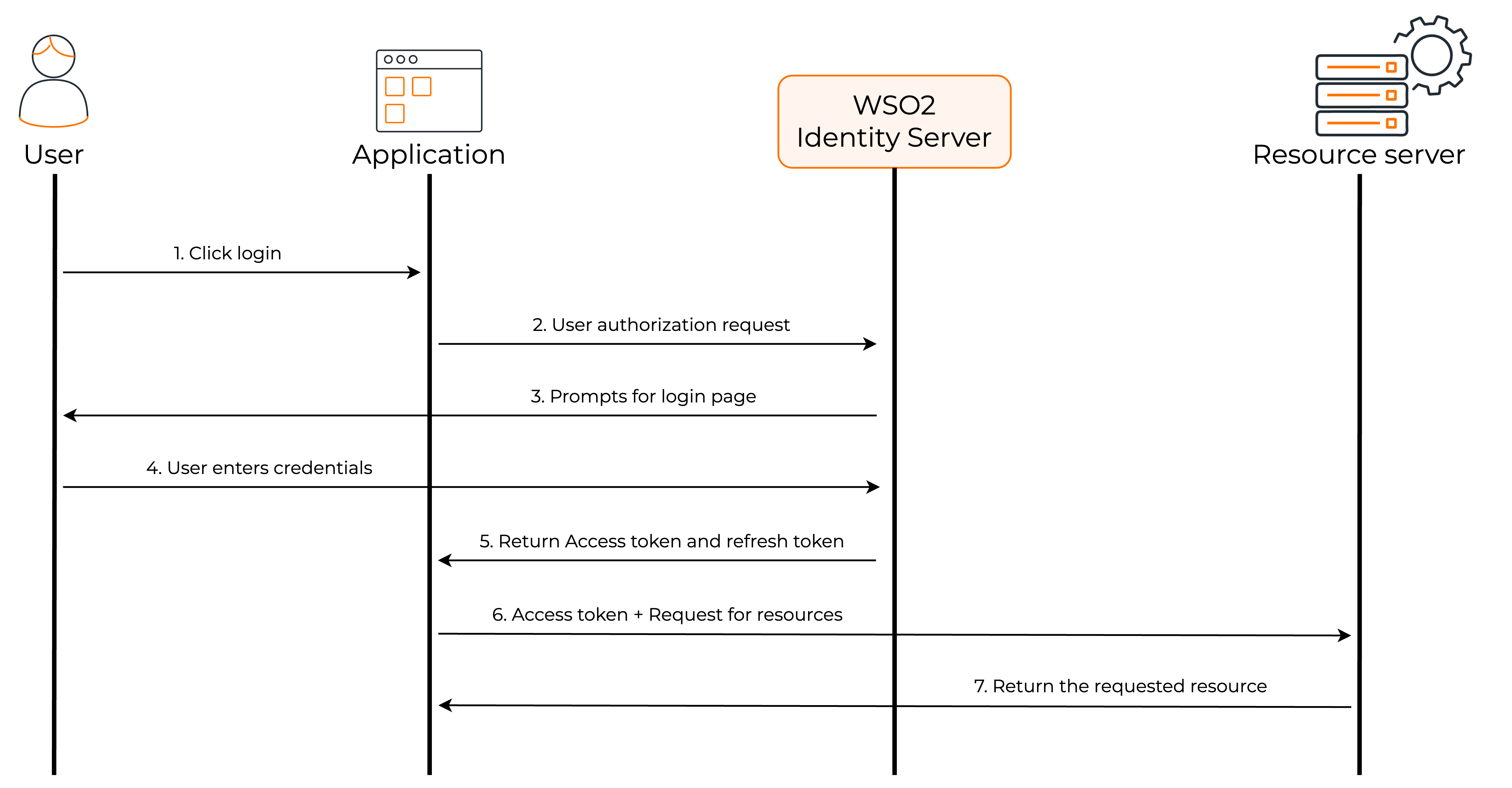
- The user visits the client application and requests for login through WSO2 Identity Server.
- The client application redirects the authorization request to WSO2 Identity Server.
- WSO2 Identity Server prompts the user to enter credentials.
- The user enters the credentials.
- After successful authentication, WSO2 Identity Server sends the access token to the client application.
- The client application can now request user information from the resource server by providing the access token.
- The resource server returns requested user information to the client application.
Password grant¶
The password grant flow is an OAuth 2.0 grant type that enables a client application to obtain an access token by presenting the user's username and password directly to the authorization server. This flow is generally considered less secure than other grant types, as it requires the client application to handle and transmit the user's credentials.
The password grant is primarily used in scenarios where the client application is highly trusted, and the user experience is prioritized over security concerns. It is generally not recommended for use in public-facing applications or scenarios where sensitive data is accessed.
The following diagram shows how the password grant flow works.
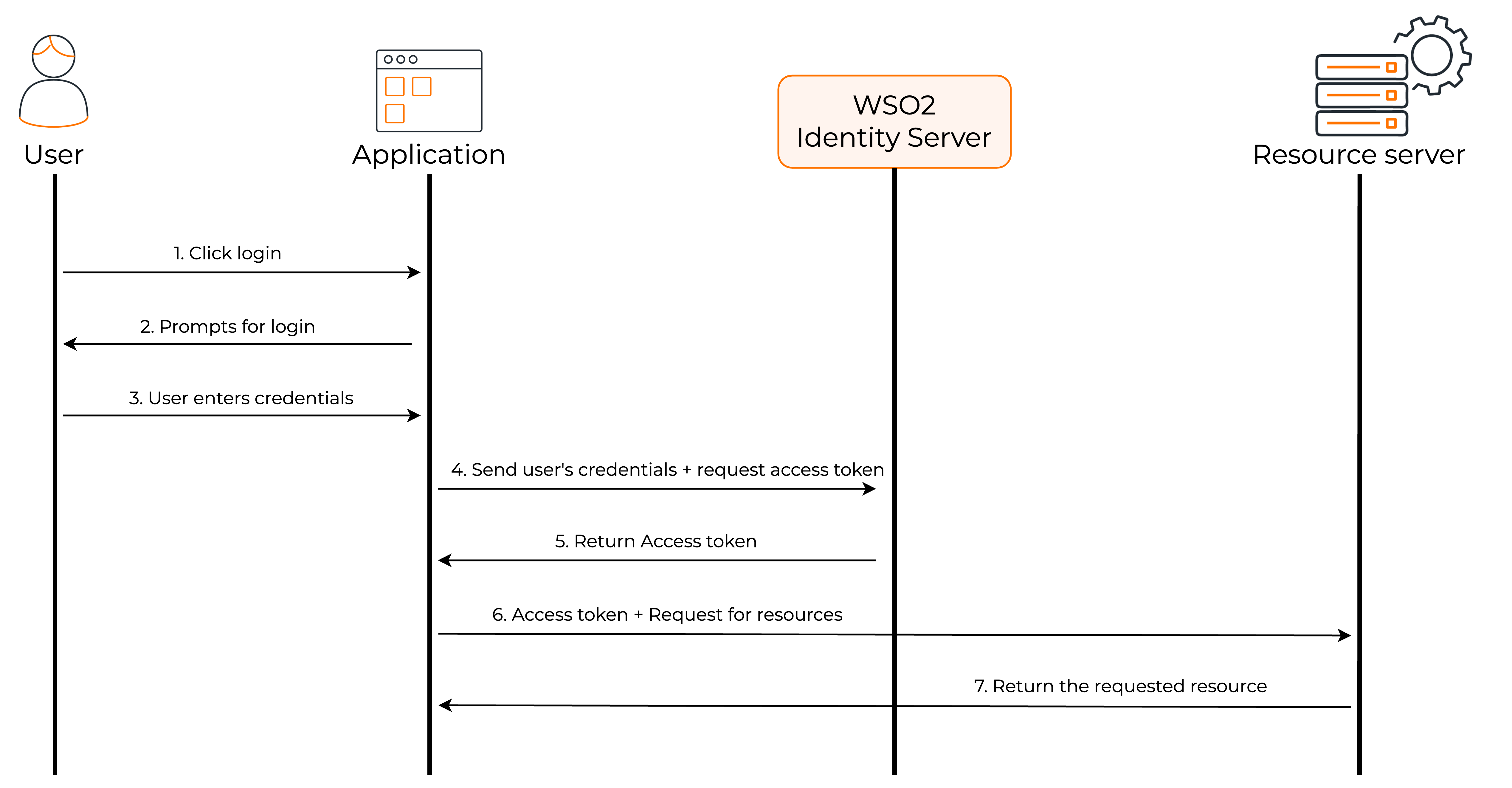
- The user visits the client application and requests for login through WSO2 Identity Server.
- The client application requests the user's credentials.
- The user sends the requested credentials to the client application.
- The client application sends the user's credentials and requests an access token from WSO2 Identity Server.
- WSO2 Identity Server sends the access token to the client application.
- The client application can now request user information from the resource server by providing the access token.
- The resource server returns the requested user information to the client application.
Token exchange grant¶
OAuth 2.0 token exchange is a grant type in the OAuth 2.0 framework that enables the exchange of one type of token for another. This grant type is defined in the OAuth Token Exchange specification (RFC 8693)
The token exchange grant type is useful in scenarios where an application needs to obtain a different type of access token with a different set of permissions or attributes than the one it currently possesses. It allows an application to act on a user's or another entity's behalf, obtaining a new access token that represents the requested authorization.
Important
Currently, WSO2 Identity Server supports the following capabilities of the OAuth 2.0 Token Exchange specification:
- Impersonation semantics of the OAuth 2.0 token exchange grant type.
- Exchanging JWT security tokens in the token exchange flow.
The following diagram shows how the token exchange grant flow works.
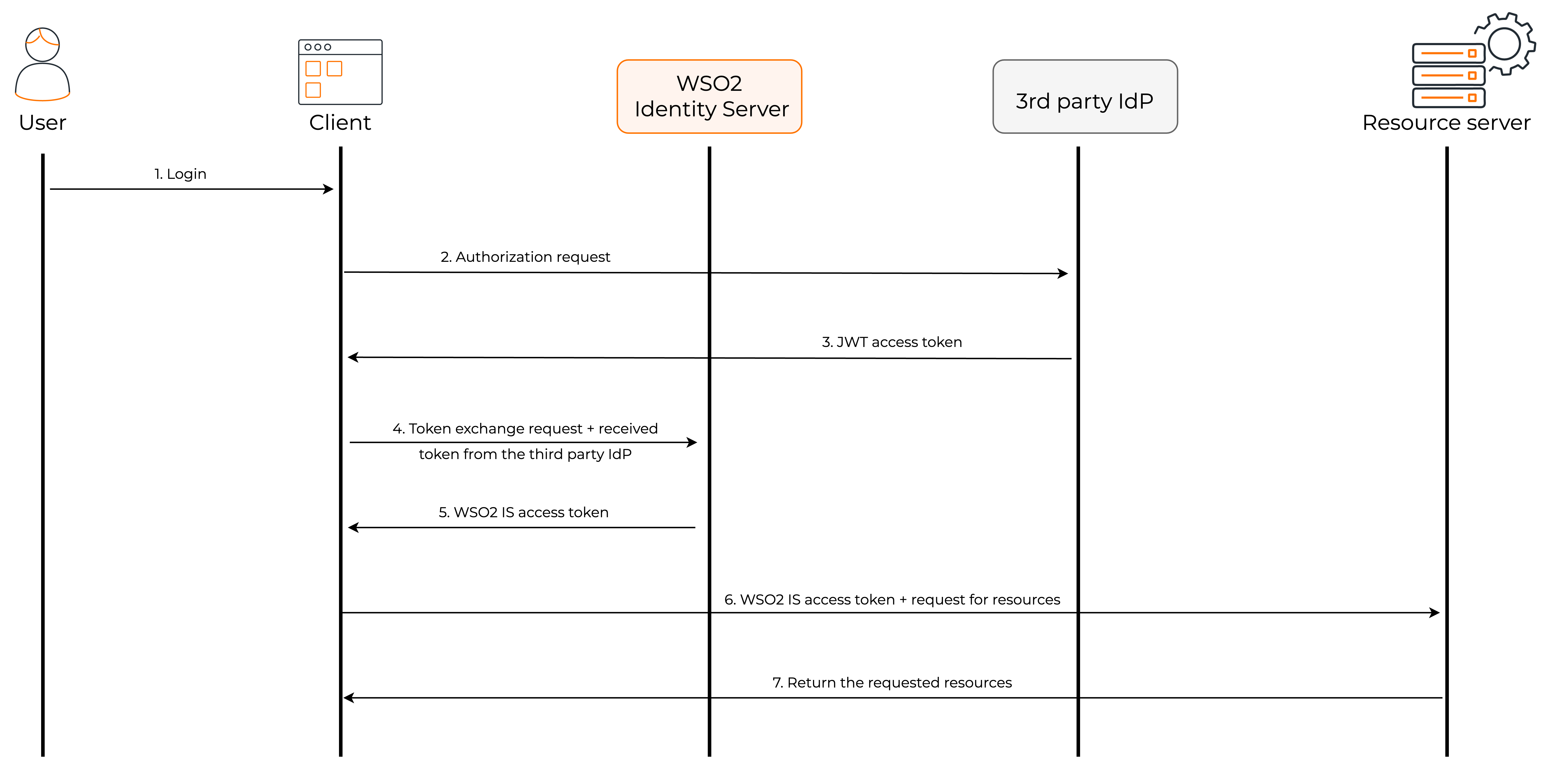
- The user sends a login request to the client application.
- The client application sends an authorization request to the third-party IdP.
- The third-party IdP returns the JWT access token for the user to the client application.
- The client application makes a token exchange request to the authorization server, specifying the Token Exchange grant type and providing the necessary parameters, such as the original access token.
- The authorization server validates the request, performs the token exchange, generates a new access token of the requested type based on the provided parameters and the server's policy, and responds to the client with the new access token.
- The client application can now request resources from the resource server by providing the access token.
- As the resource server trusts WSO2 Identity Server issued tokens, it returns the requested resources to the client application.
See configure the token exchange flow for more details.
SAML 2.0 bearer grant¶
SAML 2.0 bearer grant is a grant type in the OAuth 2.0 framework that enables the exchange of a SAML 2.0 assertion for an OAuth 2.0 access token. This grant type is defined in the SAML 2.0 Profile for OAuth 2.0 Client Authentication and Authorization Grants specification (RFC 7522)
The SAML 2.0 bearer grant is a secure method that allows clients to obtain an OAuth 2.0 access token by presenting a SAML 2.0 assertion. This grant type is particularly useful in scenarios where the client already has a SAML assertion from a trusted identity provider and seeks to exchange it for an access token. It offers significant advantages in systems that already utilize SAML for Single Sign-On (SSO), as it enables the client to obtain an access token without requiring the user to re-authenticate. To use this grant type, the client submits a request with the SAML assertion to the token endpoint, and following successful authentication and validation, the server issues an access token.
The following diagram shows how the token exchange grant flow works.
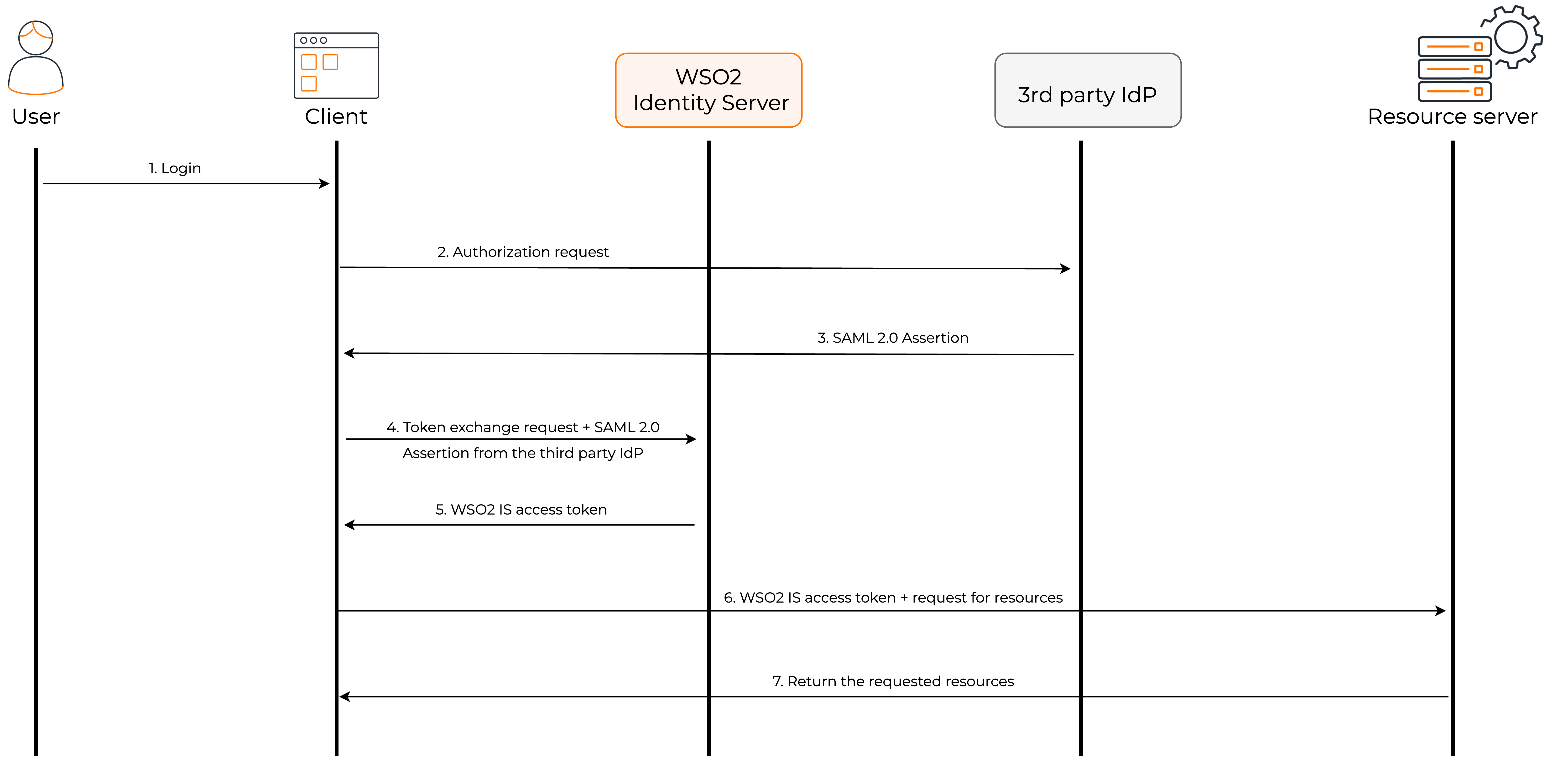
- The user sends a login request to the client application.
- The client application sends an authentication request to the third-party IdP using SAML 2.0.
- Upon successful user authentication, the third-party IdP issues a SAML 2.0 assertion to the client application.
- The client application makes a token exchange request to the authorization server, specifying the SAML 2.0 bearer grant type and providing the necessary parameters, such as the original SAML 2.0 assertion.
- The Authorization Server validates the SAML 2.0 assertion and if valid, generates a new access token of the requested type based on the provided parameters and the server's policy, and responds to the client with the new access token.
- The client application can now request resources from the resource server by providing the access token.
- As the resource server trusts WSO2 Identity Server issued tokens, it returns the requested resources to the client application.
Organization switch grant¶
The organization switch grant is a custom grant type in WSO2 Identity Server that enables users to switch between different organizations in a hierarchical organization structure.
Client applications should always use one of the traditional grant types to authorize user access. The organization switch grant is also required when the authorization request is for resources of an organization. That is because it is necessary to switch between the organization (root) and the organization to obtain access tokens that are valid for organizations.
The following diagram illustrates this flow.
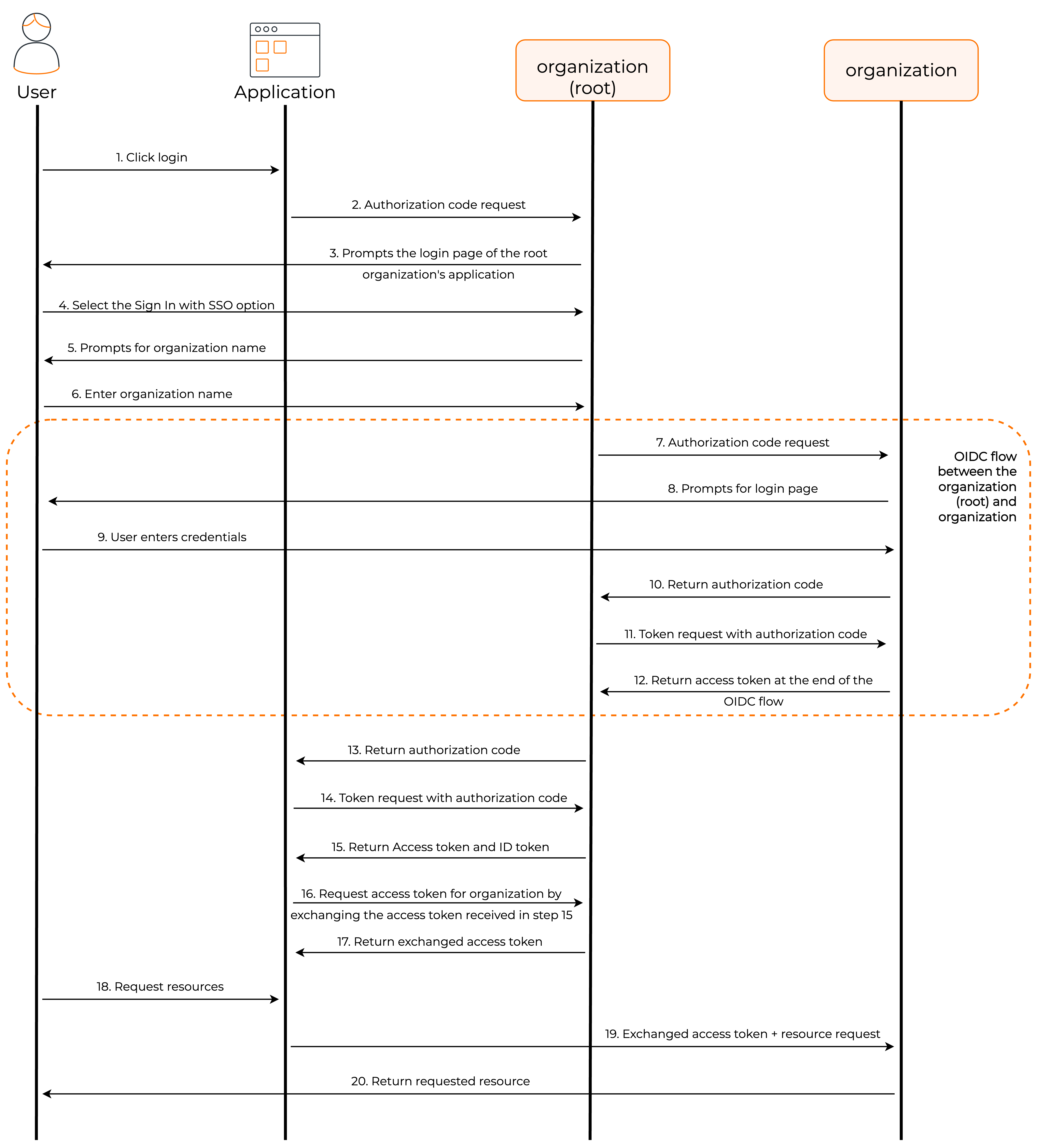
- The user visits the client application and requests login through the organization (root).
- The client application redirects the authorization code request to the organization (root).
- WSO2 Identity Server prompts the login page of the root organization's application.
- The user selects the SSO authentication option.
- The organization (root) prompts the user to enter the organization name.
- The user enters the organization name.
- The organization (root) sends an authorization code request to the organization.
- The organization prompts the user to enter credentials.
- The user enters the credentials.
- The organization sends the authorization code to the organization (root).
- The organization (root) uses this authorization code to request an access token from the organization.
- The organization sends the access token and ID token to the organization (root).
-
The organization (root) sends the authorization code to the client application.
Note
This is the response to the authorization code request in step two.
-
The client application uses this authorization code to request an access token from the organization (root).
- The organization (root) sends the access token and ID token to the client application.
- The client application exchanges the access token received in the above step for an access token for the organization.
- The organization (root) initiates an exchange for an access token and sends an access token against the organization to the client application.
- The user requests information from the client application.
- The client application requests user information from the organization by providing the access token received in step 17.
- The organization returns requested user information to the client application.