Enabling Mutual SSL¶
How it works¶
In contrast to the usual one-way SSL authentication where a client verifies the identity of the server, in mutual SSL the server validates the identity of the client so that both parties trust each other. This builds a system that has a very tight security and avoids any requests made to the client to provide the username/password, as long as the server is aware of the certificates that belong to the client.
Before the process begins the client and servers certificates are stored
in there relevant keystores . In the case of JAVA
they are jks files. Let's take a look at where the
JKS files are saved:
- WSO2 Identity Server certificates are stored in the
<IS-HOME>/repository/resources/security/wso2carbon.jksfile. - Server side certificates are stored in the
<IS-HOME>/repository/resources/security/clienttruststore.jksfile.
These certificates are signed and issued by a certificate authority that allows both the client and server to communicate freely. Now let's look at how it works:
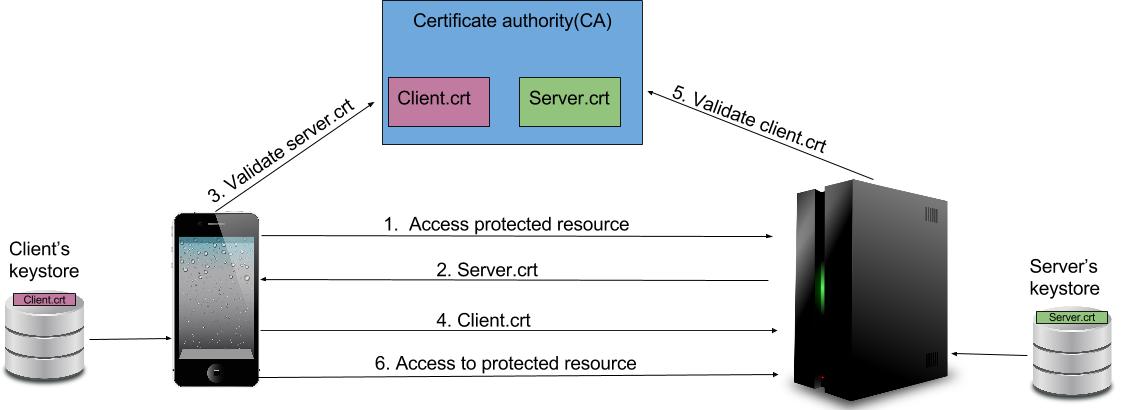
- The Client attempts to access a protected resource and the SSL/TSL handshake process begins.
- The Server presents its certificate, which is the
server.crtaccording to our example as shown above. - The Client takes this certificate and asks the certificate issued authority for the authenticity and validity of the certificate.
- If the certificate is valid, the client will also provide its certificate to the server.
- The Server takes this certificate and asks the certificate issued authority for the authenticity and validity of the certificate.
- The Client is granted access to the resource it was trying to access earlier.
Enabling Mutual SSL in the WSO2 IS¶
-
Open the
<IS_HOME>/repository/conf/tomcat/catalina-server.xmlfile and ensure that thecertificateVerificationattribute in theSSLHostConfigtag underhttpsconnector is set towantas shown below. This is done to disable the certificate authentication on certain occasions (like when working on mobile apps). This makes two-way SSL authentication optional.
If not add the following configuration tocertificateVerification="want"<IS_HOME>/repository/conf/deployment.toml[transport.https.sslHostConfig.certificate.properties] certificateVerification = "want" -
Open the
deployment.tomlfile and add the following configuration to enable the Mutual SSL Authenticator.[admin_console.authenticator.mutual_ssl_authenticator] enable = true [admin_console.authenticator.mutual_ssl_authenticator.config] WhiteList = "" -
For mutual SSL authentication, the public certificate of the WSO2 Identity Server has to be imported to the truststore of the client and the public certificate of the client has to be imported to the client-truststore of Identity Server.
Sample commands
The following two commands are examples if you are using the keystore and client-truststore of the Identity Server itself for the client. This is executed from the
<IS_HOME>/repository/resources/securitydirectory.keytool -export -alias wso2carbon -file carbon_public2.crt -keystore wso2carbon.jks -storepass wso2carbonkeytool -import -trustcacerts -alias carbon -file carbon_public2.crt -keystore client-truststore.jks -storepass wso2carbon