Integrating with Fraud Detection, Risk Based Authentication, Identity Verification and Business Intelligence Systems¶
Overview¶
Fraud Detection¶
Fraud detection is a set of activities undertaken to prevent information from being acquired under false pretenses. Fraud detection can be applied to many industries such as banking and insurance. In banking industry, fraud may include forging checks or credit card thefts. In e-commerce and retail industry, fraudulent activities mainly circles around fraud in purchases which can be any type of illegal or false transactions. When it comes to enterprise systems, fraudulent activities include identity theft and system intrusions. A system intrusion is an intentional attempt to access/modify unauthorized information in the system and convert the system to an unreliable state through information leakage or denial-of-service attacks.
Fraud detection involves monitoring the behavior of users in order to estimate anomalous behavior. These behaviors can have multiple facets including fraud, intrusion, account defaulting, and delinquency. Presently, fraud detection has been implemented by utilizing various methods such as data mining, statistics, and artificial intelligence. All of these methods analyze patterns and data about users to identify and prevent suspicious behavior.
In terms of specific industries, the methods and processes used for fraud detection can differ. In Enterprise Fraud Management(EFM) systems, fraud detection involves real-time screening of transaction activities across users, accounts, processes, and channels. E-Commerce and Retail Fraud Management (ERFM) systems occupy real-time data analysis to identify inconsistencies in customer behavior such as making large purchases at a single time, making a higher number of small transactions in a specific period, and the same person using multiple credit cards.
Risk-Based Authentication¶
Password-based authentication is still one of the primary authentication mechanisms in most of the enterprise systems . It is highly insecure and is prone to phishing attacks. Therefore, organizations should enforce additional security measures to ensure the security of their users. Multi-factor authentication is a widely accepted mechanism to enhance the security of user authentication. However, it is not a popular choice among users due to the negative impact it has on user experience. Risk-based authentication (RBA) is another mechanism that provides secure authentication while having a minimal impact on user experience. Furthermore, it ensures protection from security risks such as password database leaks, credential stuffing, insecure passwords, and guessing attacks.
RBA is an adaptive authentication mechanism which applies different authentication levels to a user, based on a risk factor associated with the user. This risk factor can be used as a deciding point when predicting the probability of a system compromise. As the risk increases, the process of authentication should become more strict and comprehensive.
RBA systems work by analysing additional properties of the user, which are contextually available during login. These include the login device, geolocation, IP address, etc. Based on these properties, a risk score is calculated for the user. This risk score is classified and based on the severity level, and additional authentication factors are requested from the user. Examples for additional authentication factors are Email/SMS-based verification, prompting CAPTCHA and so on.
Identity verification¶
Presently, data breaches are a major concern when it comes to ensuring the security of a system, as it provides means for identity impersonation. This allows fraudulent users to get easy-access to your system. Therefore, it is important to verify the identity of a user prior to user onboarding.
The Identity of a person refers to a set of attributes that can be used to describe a person uniquely. These include personal details of the user such as name, date of birth, gender, ethnicity, and it cal also relate to location or communication-based attributes such as email, home-address, mobile number etc.
Identity verification is about validating these attributes and assuring that users are who they claim to be. For verification it is desirable to use legal identities such as national identity card, driver’s license, passports, birth certificates, etc., or biometric means such as fingerprints, voice, or face recognition.
Many enterprises use identity verification (IDV) services to ensure that users provide information that is associated with the identity of a real person. These IDV services communicate with trusted sources such as legal authoritative systems to retrieve accurate information. Apart from using trusted sources, these services also engage artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to gather behavioral insights about the users.
Business Intelligence¶
Business intelligence (BI) comprises the strategies and technologies used by enterprises for the data analysis of business information. It helps to investigate insights and trends about the business for scaling and adapting the system. BI systems analyze business data and provide information in a presentable format which helps relevant authorities to make better business decisions. These BI systems make use of advanced technologies such as data warehouses, dashboards, ad hoc reporting, data discovery tools and cloud data services. They consume sales, production, financial and many other sources of business data in order to provide predictive insights to the business. Further, they collect information corresponding to other enterprises in the same industry for benchmarking.
Some use-cases where BI systems are applicable are listed below.
- Aggregating user data such as their attributes including location, device, gender, and so on, preferences, and behavioral patterns to provide product recommendations.
- Identifying your system's peak revenue time. E.g. finding ROI of a CRM system
- Tracking employee retention
- Tracking customer retention
Note
It is important for an authentication platform to have fraud detection, RBA and IDV systems integrated in order to ensure a safe and trustworthy environment for their users. Having those strategies can help mitigate any severe impact caused to the organization in terms of finance or reputation. Integration with BI systems play a major role in making informed business decisions in an enterprise.
There are multiple vendors in the market who provide tools utilizing advanced artificial intelligence / machine learning techniques for implementing these strategies. Most of them provide APIs or libraries for any enterprise to easily integrate with them.
Integrating with WSO2¶
WSO2 Identity Server supports extensive capabilities to easily integrate with any third-party platform that provides any of the above services. There are a number of different ways to do the integration. The diagram given below depicts the architecture of the WSO2 authentication framework.
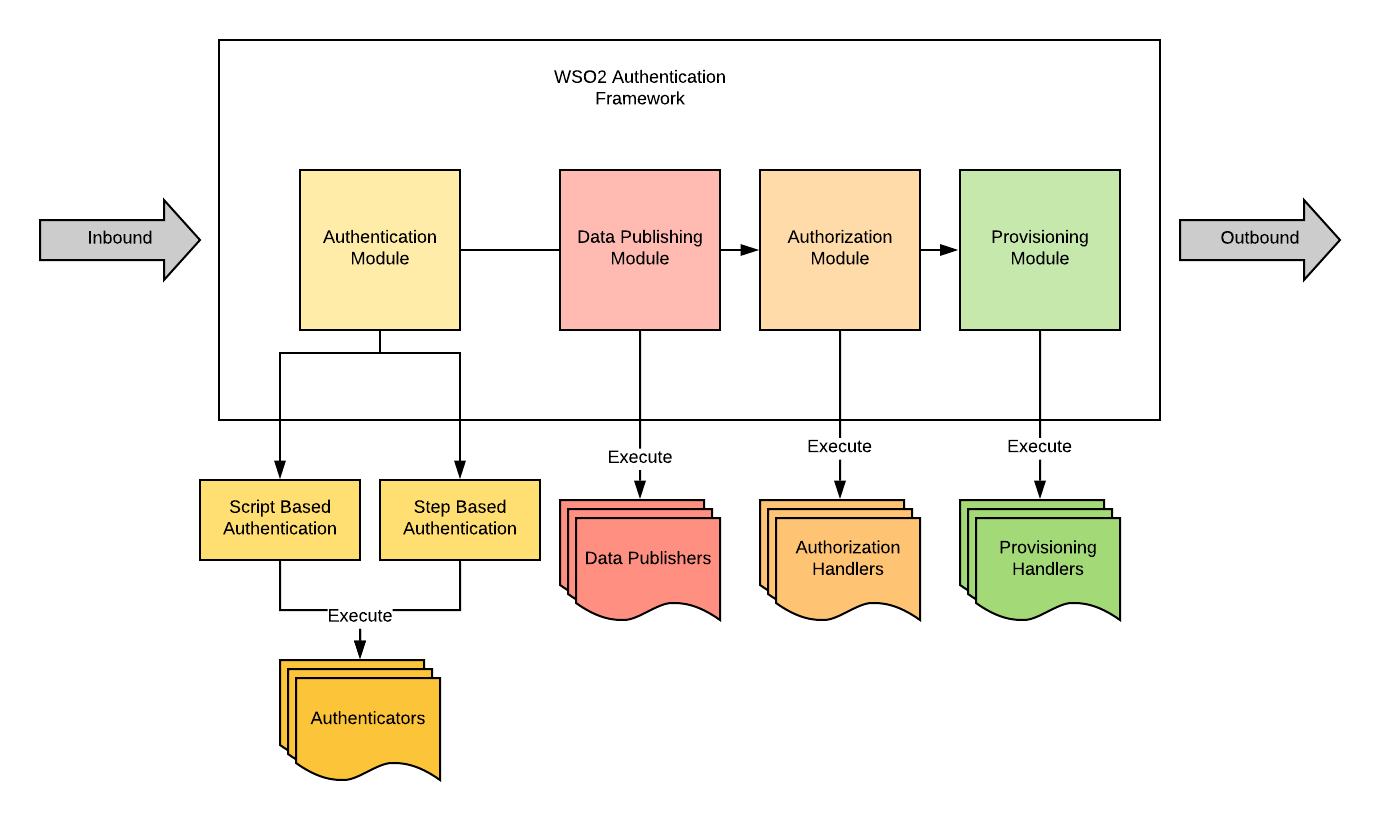
In the authentication flow shown above, the following extension points are available for integrating with an external system.
Intercepting the authentication flow based on service response¶
Custom adaptive authentication script¶
With the adaptive authentication feature in WSO2 Identity Server, it is possible to dynamically alter the authentication sequence with Javascript-based authentication schemes. WSO2 IS has some predefined javascript functions to perform authenticated user-related operations. WSO2 IS also allows you the flexibility of plugging in custom functions for desired use cases. This means that you can implement desired use-cases. Similarly we can implement a custom function to invoke a third-party system to detect fraudulent behaviors, evaluate the risk associated with the authenticated user, and also to verify the identity of the authenticated user. More details on how to write a custom adaptive function can be found here.
The following code block shows a sample script.
var onLoginRequest = function(context) {
executeStep(1, {
onSuccess: function (context) {
// Extracting authenticated subject from the first step
var user = context.currentKnownSubject;
// 'evaluateRiskScore' function will invoke a third party risk based authentication system to analyse the risk score associated with the user.
var riskScore = evaluateRiskScore(user);
if (riskScore > 7) {
Log.info(user.username + ' has a severity high risk score. Hence prompting second factor.');
executeStep(2);
}
}
});
};Custom post-authentication handler¶
Post-authentication handlers are triggered once the authentication is completed, for performing any additional post authentication tasks such as authorization. WSO2 IS also facilitates a pluggable architecture for custom handlers. You can implement a post-authentication handler by extending the AbstractPostAuthnHandler class. The post-authentication handler interface consists of a single main method which you need to implement in order to implement a post-authentication handler. More details on how to write a custom post-authentication handler can be found here.
public class CustomPostAuthenticationHandler extends AbstractPostAuthnHandler {
@Override
Public PostAuthnHandlerFlowStatus handle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse
httpServletResponse, AuthenticationContext authenticationContext) throws PostAuthenticationFailedException {
AuthenticatedUser user = authenticationContext.getLastAuthenticatedUser();
String userName = user.getUserName();
Response response = invokeExternalFraudDetectionService(userName);
// Evaluate response and decide whether to allow authentication or fail from here.
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return “CustomPostAuthenticationHandler”;
}
}Custom authenticator¶
In Identity Server, an authentication sequence can consist of multiple authentication steps.In this sequence, it is possible to incorporate additional validators in the form of a custom authenticator in addition to the standard set of authenticators that are available by default. This way, the authentication flow can be secured by ensuring the authenticity of an identity with the help of a third party fraud detection or risk-based authentication system.
The custom authenticator should be written by extending the AbstractApplicationAuthenticator class and
implementing the LocalApplicationAuthenticator. And here you need to override the process() method to invoke a third-party
service.
public class FraudDetector extends AbstractApplicationAuthenticator implements LocalApplicationAuthenticator {
@Override
protected void process(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationContext context) throws AuthenticationFailedException
{
AuthenticatedUser user = authenticationContext.getLastAuthenticatedUser();
String userName = user.getUserName();
Response response = invokeExternalFraudDetectionService(userName);
// Evaluate response and decide whether to allow authentication or fail from here.
}
@Override
protected boolean retryAuthenticationEnabled() {
return true;
}
@Override
public String getFriendlyName() {
Return "Fraud Detector"
}
@Override
public boolean canHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
Return true;
}
@Override
public String getContextIdentifier(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
return httpServletRequest.getParameter("sessionDataKey");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "FraudDetector";
}
}More information regarding how to write a custom authenticator can be found here.
Intercepting User Lifecycle Management¶
The following extension points are available in the WSO2 eventing framework to integrate with an external system and intercept user operations.
Custom event handler¶
WSO2 Identity Server supports the eventing framework which can be used to trigger some events such as user operations . Furthermore it supports pluggable handlers using which you can perform some operations based on the published events . In this manner you can intercept any user operation, invoke any third-party service and act upon the decisions provided by them. This will be the ideal extension point for integrating with BI / IDV systems. Following are some examples of events.
- PRE_AUTHENTICATION
- POST_AUTHENTICATION
- PRE_ADD_USER
- POST_ADD_USER
For integrating with a third-party identity verification solution for ensuring the authenticity of the user before registering, write a custom event handler subscribed to the PRE_ADD_USER event.
Implement a sample event handler by extending AbstractEventHandler.
Public class IdentityVerifier extends AbstractEventHandler {
@Override
public void handleEvent(Event event) throws IdentityEventException {
Map<String, Object> eventProperties = event.getEventProperties();
String userName = (String) eventProperties.get(IdentityEventConstants.EventProperty.USER_NAME);
Response response = invokeExternalIDVService(userName);
// Evaluate response and decide whether to allow registration or fail from here.
}
public String getName() {
return "IdentityVerifier";
}
@Override
public int getPriority(MessageContext messageContext) {
return 50;
}
}More information regarding WSO2 Eventing Framework Architecture can be found here
More options for intercepting user operations and triggering custom workflows are listed below.
Custom user store manager¶
In case the verification or analysis needs to be restricted to particular user store in the system, then writing a custom user store manager would be the ideal solution. Using a custom user store manager, you can intercept user store specific operations and execute custom logic. Write a custom user store manager by extending the AbstractUserStoreManager or the corresponding user store manager you need to interact with.
CustomUserstoreManager extends ReadWriteLDAPUserstoreManager {
@Override
Public void doAddUser(String userName, Object credential, String[] roleList, Map<String, String> claims, String
profileName, boolean requirePasswordChange) {
Response response = invokeExternalIDVService(userName);
// Evaluate response and decide whether to allow registration or fail from here.
If (success) {
super.doAddUser(userName, credential, roleList, claims, profileName, requirePasswordChange);
} else {
// throw exception.
}
}
}For more information on writing a custom user store manager, refer to this link.
Top